AC & DC Concepts
AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) are the two basic types of electric current used in electronics and electrical systems. Understanding AC and DC concepts is essential for studying circuits, power supplies, and electronic devices.
What is Direct Current (DC)?
Direct Current (DC) is the type of electric current in which electric charge flows in only one direction. The magnitude of current remains constant with time.
Characteristics of DC
- Flows in a single direction
- Constant magnitude
- Polarity remains fixed
Sources of DC
- Batteries
- Cells
- DC power supplies
- Solar cells
What is Alternating Current (AC)?
Alternating Current (AC) is the type of electric current in which the direction of current changes periodically with time. Its magnitude also varies continuously.
Characteristics of AC
- Direction of current changes periodically
- Magnitude varies with time
- Usually represented by a sine wave
Sources of AC
- AC generators
- Power stations
- Household electrical supply
AC and DC Waveforms
DC current is represented by a straight horizontal line on a current–time graph, showing constant current. AC current is represented by a sinusoidal waveform, showing periodic change in magnitude and direction.
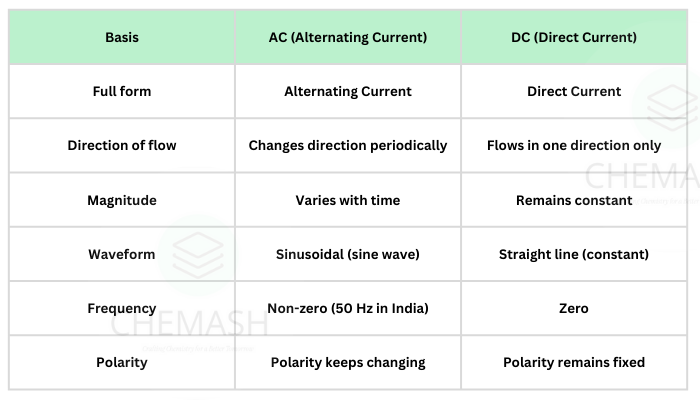
Difference Between AC and DC
| AC | DC |
|---|---|
| Direction changes periodically | Flows in one direction only |
| Magnitude varies with time | Magnitude remains constant |
| Used in household power supply | Used in electronic circuits |
| Easy to transmit over long distances | Stored easily in batteries |
Advantages of AC
- Easy voltage transformation using transformers
- Efficient for long-distance transmission
- Widely available
Advantages of DC
- Stable and constant supply
- Essential for electronic devices
- Stored easily in batteries
Applications of AC and DC
Application of AC
- Home and industrial power supply
- Electric motors
- Transmission lines
Application of DC
- Electronic circuits
- Mobile phones and laptops
- Embedded systems
- Battery-operated devices
Read related CHEMASH topics: Electronics Articles.
For a standard reference, see Wikipedia – Alternating Current.
In conclusion, AC and DC currents have different characteristics and uses. On the one hand, AC is preferred for power transmission because it is efficient over long distances. On the other hand, DC is essential for electronic devices and battery-operated systems. As a result, both AC and DC play important roles in modern technology. Thus, a clear understanding of these concepts strengthens the foundation of electronics.
Additionally, AC can be converted into DC using rectifiers for electronic circuits.
