
Acid Rain: Causes, Effects, and Solutions
Acid rain is a form of precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning it has elevated levels of hydrogen ions (low pH). It can be rain, snow, fog, hail, or even dust that contains acidic components such as sulfuric or nitric acid.
Definition
Acid rain refers to any form of precipitation with a pH lower than 5.6, typically caused by the reaction of water with sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) in the atmosphere.
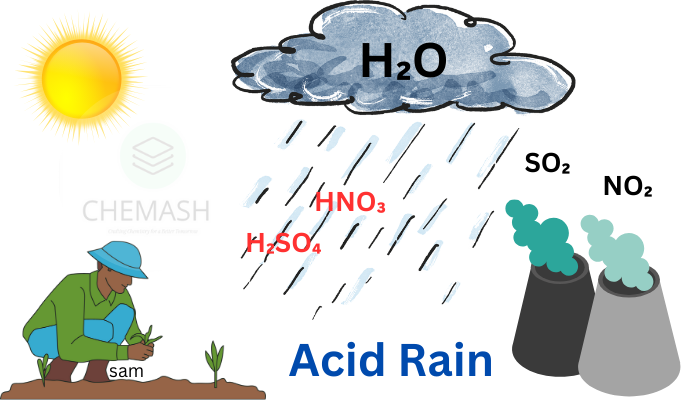
Causes
- Burning of Fossil Fuels: Coal and oil combustion releases SO₂ and NOₓ into the air.
- Vehicle Emissions: Cars, trucks, and buses emit nitrogen oxides.
- Industrial Processes: Factories and refineries contribute significantly to air pollution.
- Volcanic Activity: Natural events can also release sulfur into the atmosphere.
Effects
- Soil Degradation: Leaches nutrients from the soil, reducing fertility.
- Water Pollution: Acidifies lakes and rivers, harming aquatic life.
- Damage to Plants: Weakens trees and crops by damaging leaves and roots.
- Human Health: Indirectly affects health through air pollution (e.g., respiratory problems).
- Building Damage: Corrodes monuments, historical buildings, and infrastructure.
Solutions and Prevention
- Use of Clean Energy: Shift towards renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
- Emission Controls: Installing scrubbers in power plants and catalytic converters in vehicles.
- Afforestation: Planting trees helps absorb pollutants.
- Public Awareness: Educating people on reducing energy consumption and emissions.
Conclusion
acid rain is a serious environmental issue that requires global attention. By reducing emissions and promoting sustainable practices, we can protect ecosystems, human health, and infrastructure from its harmful effects.
MCQ
- Which gas is NOT a major contributor to acid rains?
A. Sulfur dioxide
B. Nitrogen oxide
C. Carbon monoxide
D. Both A and B
Answer: C. Carbon monoxide - What is the typical pH of acid rains?
A. 7
B. 6.5
C. Below 5.6
D. Above 8
Answer: C. Below 5.6
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is acid rain?
Acid rains is any form of precipitation—rain, snow, fog, or dust—that contains strong acids formed from sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) reacting with water vapor in the atmosphere.
Q2. What causes acid rain?
Acid rains is mainly caused by the burning of fossil fuels, vehicle emissions, industrial activities, and, to a lesser extent, natural sources like volcanic eruptions.
Q3. How does acid rains affect the environment?
Acid rains damages soil fertility, harms aquatic ecosystems, weakens plants and forests, and accelerates the corrosion of buildings and monuments.
Q4. Is acid rains harmful to humans?
Acid rains does not directly harm humans, but the pollutants that cause it can lead to respiratory problems, asthma, and other health issues.
Q5. How can acid rain be prevented?
Acid rains can be reduced by using clean energy, controlling industrial emissions, improving vehicle technology, planting trees, and conserving energy.
| Link to a trusted source (e.g. EPA on acid rain) |

Pingback: Ionic Equilibrium - CHEMASH -
Pingback: Types of pollutant affect air, water, soil, and living organisms.