Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Ionization of Carboxylic Acid
- Resonance Stabilization
- Comparison with Alcohols & Phenols
- Effect of Substituents
- Relative Acid Strength
- Quiz & Practice
- FAQ
Introduction
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds containing the carboxyl group (–COOH). They exhibit acidic behavior because the carboxyl group can donate a proton (H+) to a base.
1. Ionization of Carboxylic Acid
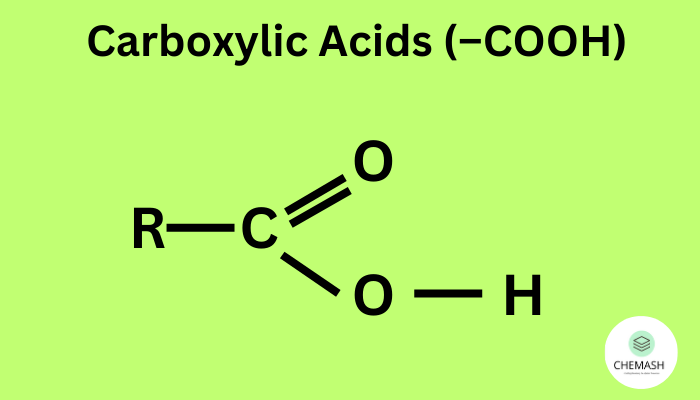
In aqueous solution, a carboxylic acid undergoes ionization as follows:
R–COOH ⇌ R–COO− + H+
The released hydrogen ion is responsible for the acidic nature of carboxylic acids.
2. Resonance Stabilization of Carboxylate Ion
The conjugate base (carboxylate ion) is stabilized by resonance:
- The negative charge is delocalized between the two oxygen atoms.
- This delocalization makes the carboxylate ion more stable than the undissociated acid.
3. Comparison with Alcohols & Phenols
Carboxylic acids are stronger acids than alcohols and phenols due to:
- Greater resonance stability of the carboxylate ion.
- Electron-withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group, making proton loss easier.
4. Effect of Substituents on Acidity
Electron-withdrawing groups (–NO2, –Cl) near –COOH increase acidity by stabilizing the negative charge.
Electron-donating groups (–CH3, –OH) decrease acidity.
5. Relative Acid Strength
Acid strength order:
Formic acid (HCOOH) > Acetic acid (CH3COOH) > Propanoic acid (CH3CH2COOH)
Note: Carboxylic acids generally have pKa values between 4–5, making them weak acids but stronger than alcohols and phenols.
Quiz & Practice
MCQs
1. Which factor makes carboxylic acids more acidic than alcohols?
- A) Hydrogen bonding
- B) Resonance stabilization ✅
- C) Higher molecular weight
- D) All of the above
Answer: Resonance stabilization of carboxylate ion.
2. Which substituent increases the acidity of carboxylic acids?
- A) –CH3
- B) –OH
- C) –NO2 ✅
- D) –CH2CH3
Answer: –NO2
True/False
Carboxylic acids are weaker acids than alcohols. ❌ (False)
Electron-donating groups reduce acidity. ✅ (True)
Fill in the Blanks
1. Carboxylic acids generally have pKa values between ___ and ___. → 4 and 5
2. The group responsible for acidity in carboxylic acids is ___ → –COOH
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why are carboxylic acids acidic?
They release a proton (H+) from the –COOH group and their conjugate base is stabilized by resonance.
2. Are carboxylic acids stronger than phenols?
Yes, because the carboxylate ion is more stabilized than the phenoxide ion.
3. What increases the acidity of carboxylic acids?
Electron-withdrawing substituents like –NO2 increase acidity by stabilizing the carboxylate ion.
