Acidity and Basicity
Acidity and basicity are key concepts in chemistry, determining the behavior of substances in digestion, cleaning, agriculture, and industries. Their properties depend on hydrogen ions (H⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻).
1. Definition
- Acid (अम्ल): Produces H⁺ ions in water. Sour taste, corrosive.
- Base (क्षार): Produces OH⁻ ions or accepts H⁺. Bitter, slippery.
2. Acid-Base Theories
- Arrhenius: Acids ↑ H⁺, Bases ↑ OH⁻ (limited to aqueous solutions).
- Brønsted–Lowry: Acids donate H⁺, Bases accept H⁺.
- Lewis: Acids = electron pair acceptors, Bases = donors.
3. pH Scale
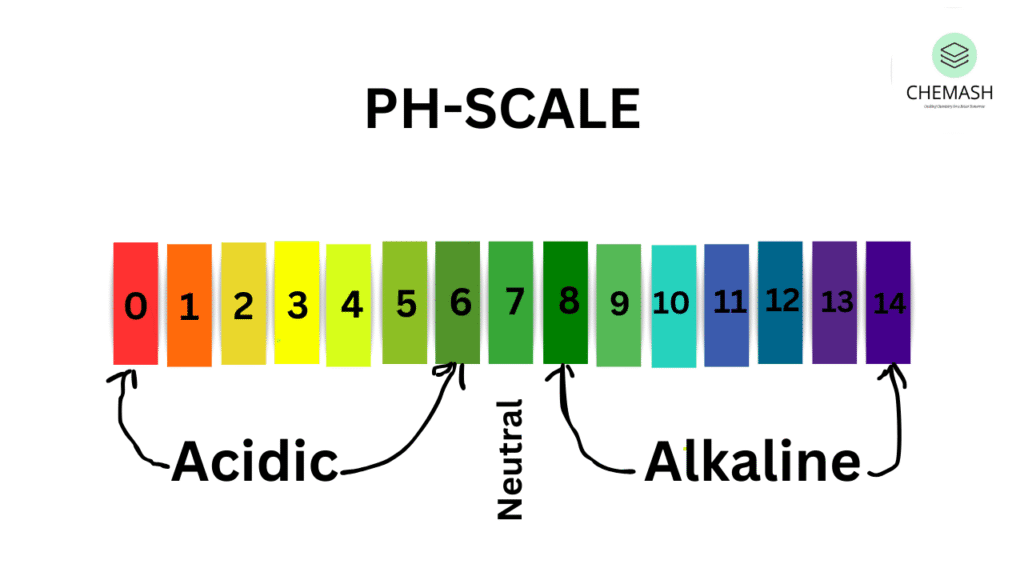
pH = -log[H⁺]
- pH 0–6.9 = Acidic
- pH 7 = Neutral
- pH 7.1–14 = Basic
4. Indicators
| Indicator | In Acid | In Base |
|---|---|---|
| Litmus | Red | Blue |
| Phenolphthalein | Colorless | Pink |
| Methyl Orange | Red | Yellow |
5. Applications
- Digestive System: HCl aids digestion.
- Antacids: Mg(OH)₂ neutralizes excess acid.
- Soil: Lime corrects acidic soil.
- Cleaning: Soaps are basic.
- Acid Rain: SO₂ + NO₂ in rainwater ↓ pH.
6. Neutralization
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
Interactive Quiz
Q1: What is the pH of a neutral solution?
- 5
- 7 ✅
- 9
- 14
Explanation: Pure water has pH 7, which is neutral.
Q2: Which indicator turns pink in base?
- Methyl Orange
- Phenolphthalein ✅
- Litmus
- Turmeric
Explanation: Phenolphthalein is colorless in acids but turns pink in bases.
True / False
- Acids taste bitter. ❌ (They are sour.)
- Bases feel slippery. ✅
Fill in the Blanks
- pH of neutral water is __7__.
- Lewis acid is an electron pair __acceptor__.
FAQs
Q1: Why is pH important?
Ans: It helps monitor health, soil, water, and industry quality control.
Q2: What is acid rain?
Ans: Rainwater with dissolved SO₂/NO₂, lowering its pH, harmful to plants and buildings.
Read about Polymers and Plastics
Learn more about pH on Wikipedia

Pingback: Strength of Acids and Bases - CHEMASH