Adsorption – Definition, Types, Applications & Differences
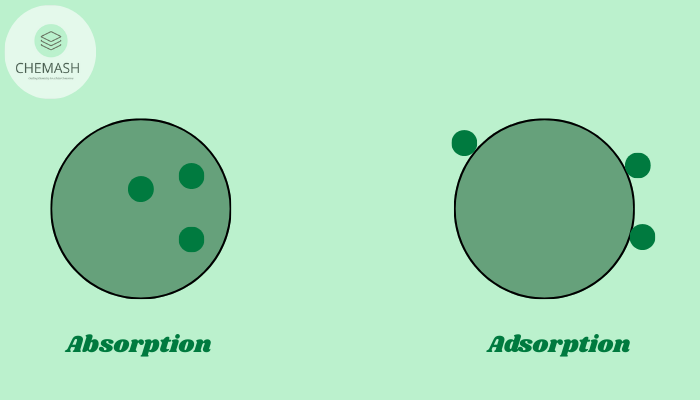
Adsorption is a surface phenomenon in which atoms, ions, or molecules from a substance (such as a gas or liquid) accumulate on the surface of a solid or liquid (adsorbent). The substance that gets accumulated is called the adsorbate. Unlike absorption, where a substance is uniformly distributed throughout the bulk, adsorption is confined to the surface.Adsorption in Chemistry
Difference Between Adsorption and Absorption
| Adsorption | Absorption |
|---|---|
| Occurs only at the surface | Occurs throughout the volume |
| Fast process initially | Slower, uniform process |
| Affected by surface area | Affected by volume of substance |
Types of Adsorption
- Physical Adsorption (Physisorption): Involves weak van der Waals forces. Reversible and occurs at low temperatures.
- Chemical Adsorption (Chemisorption): Involves chemical bonding between adsorbate and adsorbent. Stronger and often irreversible.
Factors Affecting Adsorption
- Surface area of adsorbent: Greater surface area increases adsorption.
- Nature of adsorbate and adsorbent: Some substances are more prone to adsorb specific molecules.
- Pressure (for gases): Adsorption increases with pressure (in physisorption).
- Temperature: Generally decreases with increasing temperature (exothermic process).
- Activation energy: High for chemisorption, negligible for physisorption.
Applications of Adsorption
- Gas masks: Activated charcoal adsorbs toxic gases.
- Water purification: Activated carbon removes impurities by adsorption.
- Heterogeneous catalysis: Catalyst surfaces adsorb reactants to speed up reactions.
- Chromatography: Separation of mixtures is based on differential adsorption.
- Vacuum creation: Adsorbent materials remove residual gases.
- Medicine: Antidotes for poisons often rely on adsorption by activated charcoal.
Conclusion: Adsorption is a critical surface process that plays a vital role in industrial chemistry, catalysis, environmental science, and medical applications. Its efficiency is closely tied to surface area, temperature, and the nature of the adsorbent and adsorbate.
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following is true about adsorption?
- 🔘 A) It occurs throughout the bulk of material
- ✅ B) It occurs only at the surface
- 🔘 C) It is an endothermic process
- 🔘 D) It does not depend on surface area
Explanation: Adsorption is a surface phenomenon, and its extent increases with surface area. It is usually exothermic.
2. Which of the following forces are involved in physical adsorption?
- ✅ A) van der Waals forces
- 🔘 B) Covalent bonding
- 🔘 C) Ionic bonding
- 🔘 D) Metallic bonding
Explanation: Physical adsorption (physisorption) involves weak van der Waals forces, making it reversible and dependent on temperature.
3. Adsorption of gases on solid surfaces is generally:
- ✅ A) Exothermic
- 🔘 B) Endothermic
- 🔘 C) Thermoneutral
- 🔘 D) Not affected by temperature
Explanation: Adsorption releases energy as the gas molecules adhere to the solid surface, hence it is exothermic.
4. Chemisorption differs from physisorption because:
- 🔘 A) It occurs only at low temperature
- 🔘 B) It is weak and reversible
- ✅ C) It involves chemical bonds
- 🔘 D) It requires no activation energy
Explanation: Chemisorption involves the formation of new chemical bonds between adsorbate and adsorbent, making it stronger and usually irreversible.
5. Which is NOT an application of adsorption?
- 🔘 A) Gas masks
- 🔘 B) Water purification
- 🔘 C) Heterogeneous catalysis
- ✅ D) Electrolysis of water
Explanation: Electrolysis is a redox process involving electric current, not related to surface adsorption phenomena.
True or False Questions on Adsorption
1. Adsorption is a bulk phenomenon that occurs throughout the volume of a material.
❌ False
Explanation: Adsorption occurs only on the surface of a material, unlike absorption which involves the entire volume.
2. Chemisorption involves the formation of chemical bonds between the adsorbate and the adsorbent.
✅ True
Explanation: Chemisorption is a type of adsorption where actual chemical bonds form, making it stronger and usually irreversible.
3. In physical adsorption, the process is usually reversible and occurs at high temperatures.
❌ False
Explanation: Physisorption occurs at low temperatures and is generally reversible because it involves weak van der Waals forces.
4. Adsorption is generally an exothermic process.
✅ True
Explanation: When particles adhere to a surface, energy is released, making the process exothermic in nature.
5. The extent of adsorption increases with an increase in the surface area of the adsorbent.
✅ True
Explanation: A larger surface area provides more active sites for molecules to adsorb, increasing the overall rate and quantity of adsorption.
6. Adsorption has no industrial significance.
❌ False
Explanation: Adsorption is extremely important in industries such as gas purification, water treatment, catalysis, and medicine.
Adsorption in Chemistry
