Air Pollution and Its Effects on Health
Air pollution is one of the most serious environmental problems affecting human health today. The presence of harmful substances in the atmosphere leads to respiratory diseases, heart problems, and even premature death. Rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increased vehicle use have significantly worsened air quality across the world. Air Pollution and Its Effects on Health
Table of Contents
- Meaning of Air Pollution
- Sources and Causes of Air Pollution
- Major Air Pollutants
- Health Effects of Air Pollution
- Short-Term and Long-Term Impacts
- Vulnerable Groups
- Prevention and Control Measures
- MCQs with Answers
- Frequently Asked Questions
1. Meaning of Air Pollution
Air pollution refers to the contamination of air by harmful gases, particulate matter, and biological molecules that are dangerous to living organisms and the environment. When pollutants exceed permissible limits, air quality becomes unsafe to breathe.
In simple terms:
Air pollution occurs when harmful substances mix with air and damage human health and ecosystems.
2. Sources and Causes of Air Pollution
Natural Sources
- Volcanic eruptions
- Forest fires
- Dust storms
- Pollen and spores
Human-Made Sources
- Automobile exhaust
- Industrial emissions
- Burning of fossil fuels
- Construction activities
- Household cooking using solid fuels
3. Major Air Pollutants
| Pollutant | Source | Health Impact |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 & PM10 | Vehicles, industries | Lung & heart diseases |
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Incomplete combustion | Reduced oxygen supply |
| Sulphur Dioxide (SO₂) | Coal burning | Asthma & bronchitis |
| Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) | Vehicles | Lung irritation |
| Ozone (O₃) | Photochemical reactions | Chest pain & coughing |
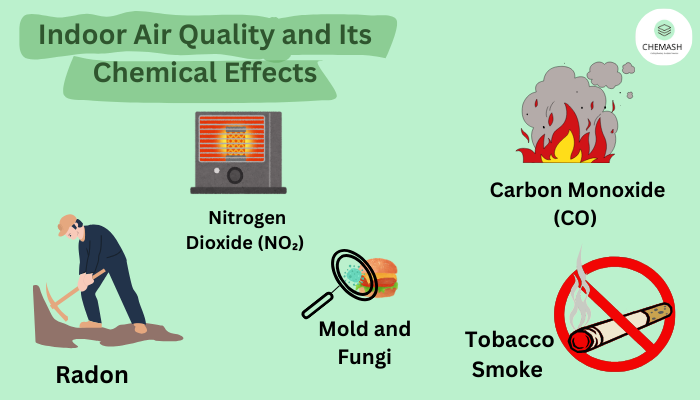
4. Effects of Air Pollution on Human Health
Exposure to polluted air affects almost every organ of the human body. The severity depends on pollutant concentration, exposure time, and individual sensitivity.
Respiratory System
- Asthma attacks
- Chronic bronchitis
- Reduced lung capacity
Cardiovascular System
- Heart attacks
- High blood pressure
- Irregular heartbeat
Nervous System
- Headaches
- Memory loss
- Developmental disorders in children
5. Short-Term and Long-Term Health Impacts
Short-Term Effects
- Eye and throat irritation
- Coughing and sneezing
- Fatigue and dizziness
Long-Term Effects
- Lung cancer
- Chronic respiratory diseases
- Premature death
6. Vulnerable Groups
Some groups are more sensitive to air pollution:
- Children
- Elderly people
- Pregnant women
- People with asthma or heart disease
7. Prevention and Control of Air Pollution
- Use public transport and electric vehicles
- Plant more trees
- Adopt renewable energy sources
- Follow emission standards
- Avoid burning waste
Improving air quality improves overall public health and life expectancy.
8. MCQs – Air Pollution
Q1. Which pollutant affects lungs most severely?
- A. Carbon dioxide
- B. PM2.5 ✅
- C. Nitrogen
- D. Oxygen
Explanation: Fine particulate matter enters deep into lungs.
Q2. Major source of urban air pollution is:
- A. Volcanoes
- B. Oceans
- C. Vehicles ✅
- D. Forests
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is air pollution?
It is contamination of air by harmful substances.
How does air pollution affect health?
It causes respiratory, cardiovascular, and neurological diseases.
Can air pollution be prevented?
Yes, through clean energy, reduced emissions, and awareness.
External Reference: WHO – Air Pollution
