Alcohols in Organic Chemistry
Introduction
Alcohols are a class of organic compounds containing one or more hydroxyl (–OH) groups attached to a saturated carbon atom. They play vital roles in industrial applications, biological systems, and laboratory synthesis.
General Characteristics
- Functional Group: –OH (hydroxyl group)
- General Formula: CnH2n+1OH
- Nature: Polar due to the presence of hydrogen bonding
Classification
Based on Number of –OH Groups
- Monohydric: One –OH group (e.g., Ethanol)
- Dihydric: Two –OH groups (e.g., Ethylene glycol)
- Trihydric: Three –OH groups (e.g., Glycerol)
Based on Carbon Attachment
- Primary (1°): –OH attached to a primary carbon
- Secondary (2°): –OH attached to a secondary carbon
- Tertiary (3°): –OH attached to a tertiary carbon
Nomenclature
- Common Names: Methyl alcohol, Isopropyl alcohol
- IUPAC Names: Methanol, Ethanol (CH3CH2OH)
Physical Properties
- High boiling points due to strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding
- Lower alcohols are miscible in water
- Volatile and flammable in nature
Preparation Methods
- Hydration of Alkenes: Alkene + H₂O → Alcohol
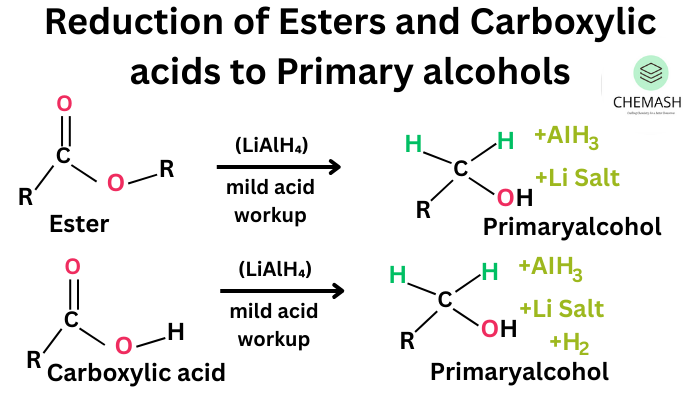
- Reduction of Aldehydes/Ketones: Using LiAlH₄ or NaBH₄
- Hydrolysis of Alkyl Halides: R–X + H₂O → R–OH
- Fermentation: Glucose → Ethanol + CO₂
Chemical Reactions
- Reaction with Sodium: Produces alkoxide and hydrogen gas
- Dehydration: Forms alkenes using concentrated H₂SO₄
- Oxidation: Converts to aldehydes, ketones, or acids depending on class
- Esterification: Reacts with carboxylic acids to form esters
Applications
- Used in beverages (ethanol)
- Solvent in pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries
- Key ingredient in sanitizers and antiseptics
- Used as a biofuel (ethanol blended with petrol)
- Intermediate in synthesis of dyes, plastics, and drugs
Did you know? Glycerol, a trihydric alcohol, is widely used in skincare products due to its excellent moisturizing properties and is also a byproduct of biodiesel production.
Quick MCQ Quiz
- Which of the following is a trihydric alcohol?
a) Methanol
b) Ethanol
c) Glycerol ✅
d) Propanol - Primary alcohols on oxidation give:
a) Ketones
b) Aldehydes ✅
c) Carboxylic acids
d) Esters - Which reagent is used for the reduction of aldehydes to alcohols?
a) H₂SO₄
b) LiAlH₄ ✅
c) NaCl
d) KMnO₄ - The functional group of alcohol is:
a) –COOH
b) –OH ✅
c) –CHO
d) –C≡N - Ethanol can be produced by:
a) Fermentation ✅
b) Combustion
c) Hydrogenation
d) Neutralization
True/False
- Alcohols have lower boiling points than alkanes of similar molecular weight.
❌ False – They have higher boiling points due to hydrogen bonding. - All alcohols are soluble in water.
❌ False – Only lower alcohols are miscible with water. - Ethanol is used as a biofuel.
✅ True
