Applications of Surface Chemistry
Surface chemistry deals with phenomena occurring at the surfaces or interfaces of materials. It plays a crucial role in various natural and industrial processes, influencing how substances interact and behave. Below is a comprehensive guide to its real-world applications:
1️⃣ Catalysis
One of the most significant applications of surface chemistry is in heterogeneous catalysis, where reactions occur on the surface of a solid catalyst. Reactants adsorb onto the surface, react, and then desorb as products.
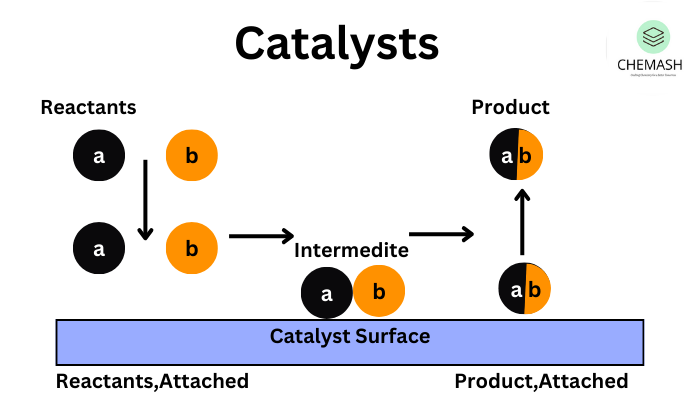
- Example: Platinum or palladium in automobile catalytic converters to reduce pollution.
- Example: Haber’s process for ammonia synthesis using iron catalyst.
2️⃣ Adsorption-Based Purification
Surface chemistry enables purification of gases and liquids by adsorbing impurities onto solids like activated charcoal or silica gel.
- Gas masks remove toxic gases using adsorption.
- Activated charcoal in water and air purification systems.
3️⃣ Medicines and Drug Delivery
Many drugs are designed based on adsorption characteristics. Controlled-release formulations use surface adsorption to deliver drugs gradually.
- Activated charcoal as an antidote for poisoning.
- Surface-functionalized nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery.
4️⃣ Cleaning Agents and Soaps
Detergents, soaps, and emulsifiers operate by reducing surface tension and adsorbing dirt and grease, enabling easy removal.
- Soaps form micelles that trap oily dirt.

5️⃣ Chromatography
This analytical technique is based on the differential adsorption of substances on a solid adsorbent and their movement with a liquid or gas phase.
- Used for separation and identification of mixture components in labs and industries.
6️⃣ Paints, Dyes, and Inks
Surface properties influence the adhesion and durability of paints and inks, with adsorption ensuring uniform spreading.
7️⃣ Metallurgical Applications
Processes like froth flotation separate ores based on differences in surface wettability.
8️⃣ Environmental Control

- Adsorbents trap harmful pollutants to reduce air and water pollution.
- Oil spills treated with adsorbent materials to remove hydrocarbons.
9️⃣ Sensors and Detection Devices
Modern sensors use surface chemistry to detect trace amounts of gases, ions, or biomolecules through measurable surface interactions.
Conclusion: Surface chemistry is foundational to numerous fields such as catalysis, environmental protection, medicine, metallurgy, and analytical sciences. Understanding it drives innovation in material science and technology.
Quick MCQ Quiz
- Which process uses adsorption in purification?
a) Distillation
b) Chromatography
c) Gas masks ✅
d) Crystallization - The catalyst in Haber’s process is:
a) Platinum
b) Nickel
c) Iron ✅
d) Copper - Micelles are formed by:
a) Acids
b) Soaps ✅
c) Metals
d) Plastics - Which technique relies on differential adsorption?
a) Filtration
b) Chromatography ✅
c) Evaporation
d) Centrifugation - Oil spills are treated using:
a) Catalysts
b) Adsorbents ✅
c) Surfactants
d) Oxidizing agents
True / False
- Surface chemistry has no role in environmental control. ❌ (False – It helps remove pollutants and oil spills)
- Chromatography works due to adsorption. ✅ (True)
- Froth flotation is unrelated to surface properties. ❌ (False – It depends on wettability differences)
