Atomic Number and Mass Number
Atoms are identified by two key numbers: the atomic number and the mass number. These values define an element’s identity and characteristics. For more basics, see our guide on Mole Concept (internal link).
1. Atomic Number (Z)
The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. It defines the element and its position in the periodic table.
- Symbol: Z
- Equal to number of protons.
- In a neutral atom, also equals electrons.
- Determines chemical properties.
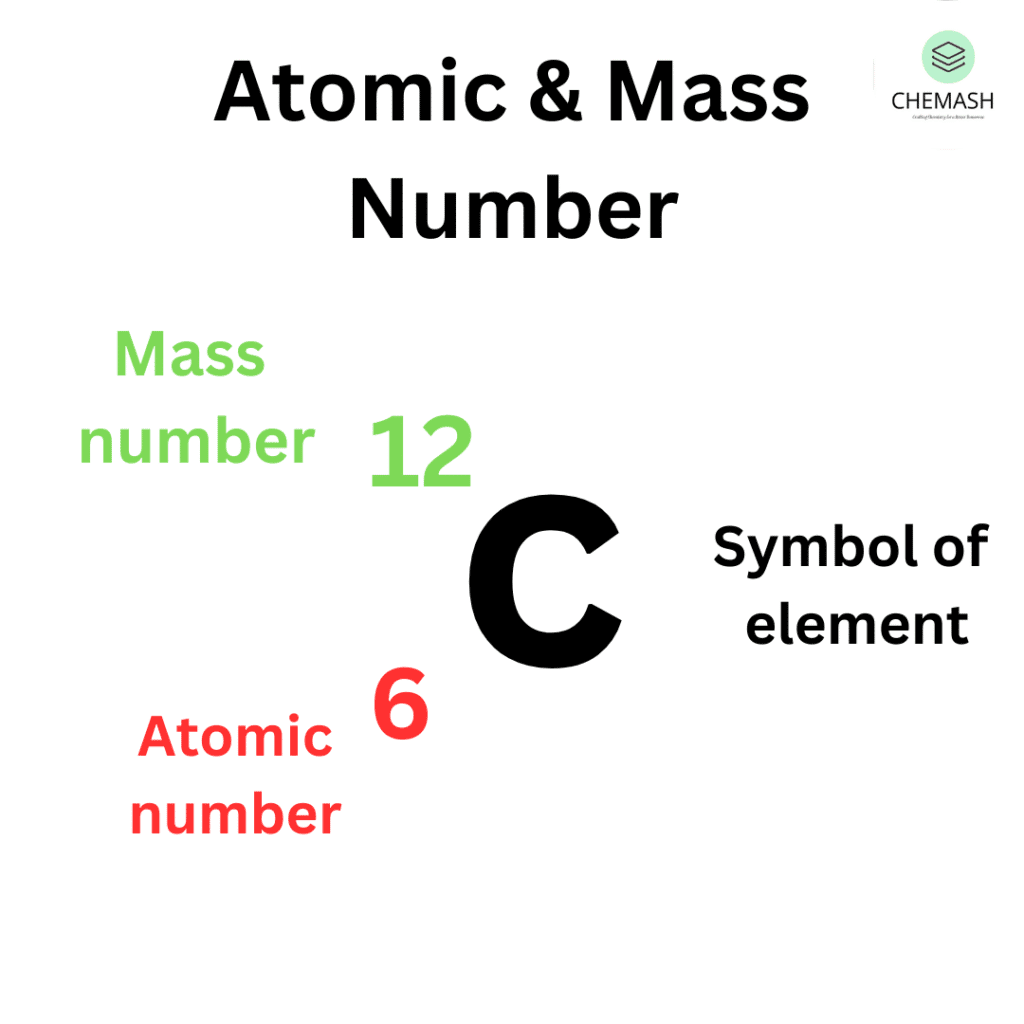
Example: Hydrogen → Z = 1, Carbon → Z = 6.
2. Mass Number (A)
The mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
- Symbol: A
- Formula: A = Protons + Neutrons
- Always a whole number
- Varies for isotopes
Example: Carbon-12 → A=12 (6p + 6n), Carbon-14 → A=14 (6p + 8n).
3. Relation Between Z, A, and Neutrons
Number of neutrons (n) can be calculated as:
n = A – Z
4. Atomic Notation
Atoms are written as:
AZ X
Example: Carbon-12 → 126C
5. Isotopes, Isobars, Isotones
- Isotopes: Same Z, different A (e.g., Carbon-12 & Carbon-14).
- Isobars: Same A, different Z (e.g., Argon-40 & Calcium-40).
- Isotones: Same neutrons, different Z (e.g., C-14 & N-15).
6. Importance
- Identifying elements uniquely
- Understanding isotopic composition
- Calculating average atomic mass
- Predicting nuclear stability
Quiz & Practice
MCQs
Q1: Atomic number represents?
A) Neutrons
B) Protons ✅
C) Electrons
D) Protons+Neutrons
Explanation: Atomic number = number of protons.
Q2: An atom with A=23, Z=11 is?
A) 1123Na
B) 2311Na ✅
C) 2311Mg
D) 1123Mg
Explanation: Sodium has Z=11.
Fill in the blanks
1. Atomic number is equal to the number of protons.
2. Neutrons = A – Z.
3. Isotopes differ in the number of neutrons.
FAQs
Q1: Why is mass number not shown in the periodic table?
Ans: Because isotopes of an element have different mass numbers.
Q2: What is the difference between atomic mass and mass number?
Ans: Mass number is protons + neutrons; atomic mass is the weighted average of isotopes.
Learn more on Wikipedia: Atomic Number.
