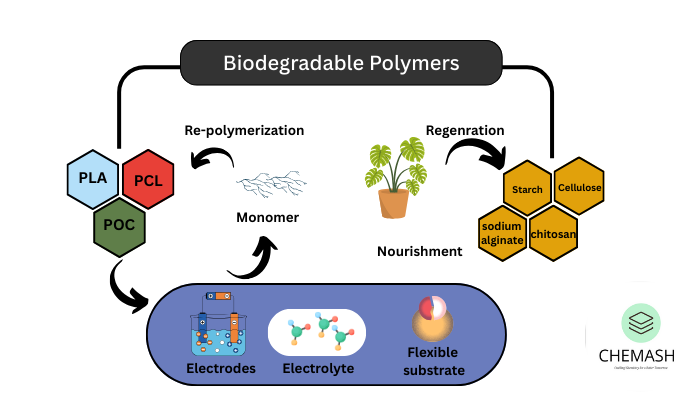
Biodegradable polymers are materials capable of breaking down into non-toxic by-products such as carbon dioxide, methane, water, and biomass through natural processes involving microorganisms. In addition, they serve as an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional plastics. Therefore, their use in packaging, agriculture, medicine, and consumer goods helps reduce plastic pollution and dependency on petrochemicals. Biodegradable Polymers
Classification of Biodegradable Polymers
- Natural Biodegradable Polymer: Obtained from natural sources. For example: Cellulose, starch, proteins, chitosan.
- Synthetic Biodegradable Polymers: Chemically synthesized with biodegradable linkages. Examples include: Polylactic acid (PLA), Polycaprolactone (PCL), Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA).
Key Biodegradable Polymer
Below are some of the most widely studied biodegradable polymers. Moreover, each plays a significant role in sustainability:
- Polylactic Acid (PLA): Made from corn starch or sugarcane. It is used in food packaging, disposable cutlery, and medical implants.
- Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA): Produced by bacteria from plant sugars. They are used in agricultural films and biodegradable plastics.
- Polycaprolactone (PCL): A biodegradable polyester used in controlled drug delivery and sutures.
- Starch-based Polymers: Derived from potato, corn, or rice starch. They are common in compostable bags and packaging foams.
- Chitosan: Extracted from chitin in crustacean shells. It finds use in wound healing and water purification.
Applications of Biodegradable Polymer
Biodegradable polymers are versatile. Consequently, they are used across many industries:
- Medical: Sutures, drug carriers, scaffolds for tissue engineering.
- Packaging: Biodegradable films, containers, and wrapping materials.
- Agriculture: Mulching films, controlled-release fertilizers, plant pots.
- 3D Printing: PLA filaments are widely used in eco-friendly 3D printing.
- Consumer Goods: Compostable bags, disposable plates, and hygiene products.
Advantages
In summary, biodegradable polymer provide several benefits:
- Reduces landfill and ocean pollution.
- Derived from renewable resources.
- Non-toxic degradation products.
- Promotes sustainable circular economy.
Challenges and Limitations
However, they are not without drawbacks:
- Higher production cost than conventional plastics.
- Limited mechanical strength and thermal stability.
- Requires industrial composting facilities for effective breakdown.
Quiz: Biodegradable Polymer
Q1. Which of the following is a synthetic biodegradable polymer?
A) Chitosan
B) Polyethylene
C) PLA
D) Cellulose
✔ Answer: C — PLA is a synthetic biodegradable polymer derived from corn starch or sugarcane.
FAQs on Biodegradable Polymer
Q1: Are biodegradable polymers cost-effective?
Answer: Currently, they are more expensive than traditional plastics. Nevertheless, mass production and technological advancements are reducing costs.
Q2: Do biodegradable plastics decompose everywhere?
Answer: No, many require industrial composting facilities. For instance, PLA needs higher temperatures to degrade efficiently.
Q3: How do biodegradable polymer help the environment?
Answer: They reduce plastic waste in oceans and landfills. Moreover, they return to natural cycles without leaving microplastics.
