Carbohydrates – Structure, Classification & Functions
Carbohydrates are one of the most important biomolecules essential for life. They serve as the primary source of energy and play key structural and metabolic roles in living organisms.
Table of Contents
- What Are Carbohydrates?
- Classification of Carbohydrates
- Functions of Carbohydrates
- Common Examples
- Biological Importance
- Exam Tips & Pitfalls
- MCQs + Answers
- True / False
- Fill in the Blanks
- FAQs
- कार्बोहाइड्रेट (Hindi)
What Are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are organic biomolecules composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). They are the most abundant organic compounds in nature and act as the primary source of energy for living organisms.
General Formula: Cn(H2O)n (mainly applicable to monosaccharides)
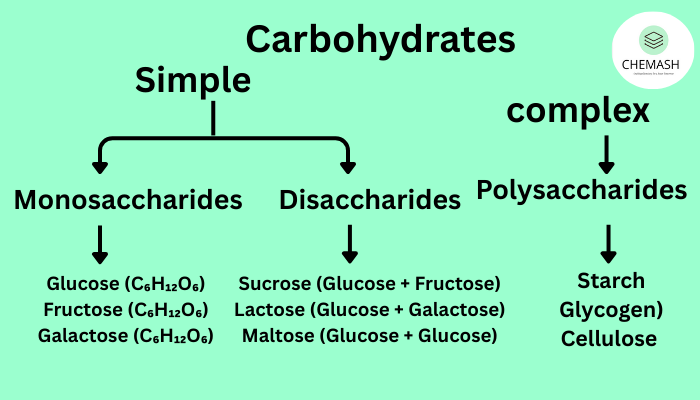
Classification of Carbohydrates
1. Monosaccharides
Simple sugars that cannot be hydrolyzed further.
- Examples: Glucose, Fructose, Galactose
2. Disaccharides
Formed by the condensation of two monosaccharide units.
- Sucrose (Glucose + Fructose)
- Lactose (Glucose + Galactose)
3. Oligosaccharides
Contain 3–10 monosaccharide units and are often involved in cell recognition.
4. Polysaccharides
Long chains of monosaccharides serving storage or structural roles.
- Starch – Plant storage
- Glycogen – Animal storage
- Cellulose – Plant cell wall
Functions of Carbohydrates
- Provide quick energy (glucose)
- Structural support (cellulose, chitin)
- Components of nucleic acids (ribose & deoxyribose)
- Main fuel for the brain and nervous system
- Act as metabolic intermediates
Common Examples
- Monosaccharides: Glucose, Fructose
- Disaccharides: Sucrose, Lactose
- Polysaccharides: Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose
Biological Importance
- Ribose forms RNA backbone
- Glycogen stores energy in liver and muscles
- Cellulose maintains plant rigidity
- Interconversion with fats during metabolism
Exam Tips & Pitfalls (NEET / CBSE)
- Do not confuse starch (storage) with cellulose (structural)
- Glucose is the main fuel of the brain
- Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar
MCQs
Q1. The general formula of carbohydrate is:
(a) CnH2nOn (b) CnH2n-2On (c) CnH2n+2On (d) None
Answer: (a)
Q2. Storage carbohydrate in animals is:
Answer: Glycogen
True / False
- Glucose is a polysaccharide ❌
- Cellulose is digestible by humans ❌
Fill in the Blanks
- Plant storage carbohydrate is Starch
- Sugar in milk is Lactose
FAQs
Why are carbohydrate called energy molecules?
They provide immediate energy in the form of glucose for ATP synthesis.
Difference between starch and cellulose?
Starch is digestible storage polysaccharide, cellulose is indigestible structural polysaccharide.
कार्बोहाइड्रेट (Hindi)
कार्बोहाइड्रेट कार्बन, हाइड्रोजन और ऑक्सीजन से बने जैविक यौगिक हैं। ये शरीर में ऊर्जा का मुख्य स्रोत होते हैं। उदाहरण: ग्लूकोज़, स्टार्च, ग्लाइकोजन।

Pingback: Proteins – Structure, Types, Functions & MCQs |
Pingback: Classification of Vitamins – Fat Soluble & Water Soluble Vitamins |