Carbohydrates – The Energy Molecules
Table of Contents
- What Are Carbohydrates?
- Classification of Carbohydrates
- Functions of Carbohydrates
- Common Examples
- Biological Importance
- Exam Tips & Pitfalls
- MCQs + Answer Key
- True / False
- Fill in the Blanks
- FAQs
- कार्बोहाइड्रेट (Hindi)
- Helpful Links
What Are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are organic biomolecules composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). They are the most abundant biomolecules on Earth and act as the major source of energy for living organisms.
General Formula: Cn(H2O)n (commonly seen in simple sugars)
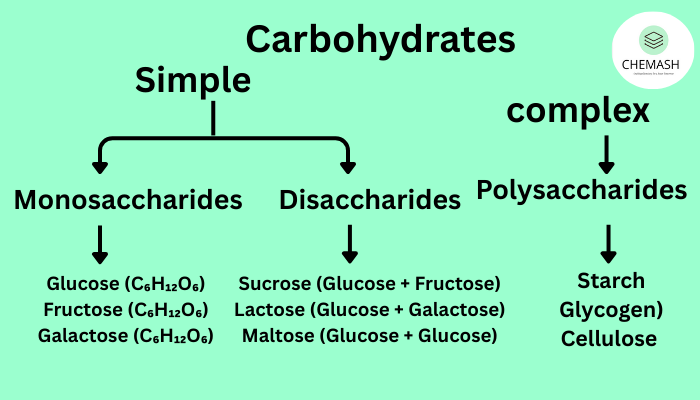
Classification of Carbohydrates
- Monosaccharides – Simple sugars (e.g., glucose, fructose)
- Disaccharides – Two monosaccharides (e.g., sucrose, lactose)
- Oligosaccharides – 3–10 monosaccharide units
- Polysaccharides – Long chains (e.g., starch, glycogen, cellulose)
Functions of Carbohydrates
- Provide quick energy (glucose is the body’s main fuel)
- Structural support (cellulose in plants, chitin in fungi)
- Component of nucleotides (ribose in RNA, deoxyribose in DNA)
- Brain fuel – preferred energy source for neurons
- Act as metabolic intermediates
Common Examples
Monosaccharides: Glucose, Fructose, Galactose
Disaccharides: Sucrose (glucose + fructose), Lactose (glucose + galactose)
Polysaccharides: Starch (plants), Glycogen (animals), Cellulose (plant cell walls)
Biological Importance
- Ribose sugar forms part of RNA backbone
- Glycogen stores energy in muscles & liver
- Cellulose maintains plant structure
- Carbohydrates interconvert with fats in metabolism
Exam Tips & Pitfalls
- Don’t confuse cellulose (structural) with starch (storage).
- Remember glucose is the main fuel for the brain.
- Monosaccharides are reducing sugars; sucrose is non-reducing.
MCQs
- The general formula of simple carbohydrates is:
(a) CnH2nOn (b) CnH2n-2On (c) CnH2n+2On (d) None
Answer: (a) CnH2nOn - Which carbohydrate is the main storage form in animals?
(a) Starch (b) Glycogen (c) Cellulose (d) Glucose
Answer: (b) Glycogen
True / False
- Glucose is a polysaccharide. ❌ (False, it’s a monosaccharide)
- Cellulose is digestible by humans. ❌ (False, humans lack cellulase)
Fill in the Blanks
- The storage carbohydrate in plants is ________. (Answer: Starch)
- The sugar present in milk is ________. (Answer: Lactose)
FAQs
Why are carbohydrates called energy molecules?
Because they provide immediate fuel (glucose) for metabolism and ATP production.
What is the difference between starch and cellulose?
Both are polysaccharides of glucose, but starch is storage (digestible), while cellulose is structural (indigestible for humans).
कार्बोहाइड्रेट (Hindi)
कार्बोहाइड्रेट कार्बन, हाइड्रोजन और ऑक्सीजन से बने जैविक यौगिक हैं। ये जीवों में ऊर्जा का प्रमुख स्रोत हैं। उदाहरण: ग्लूकोज़, सुक्रोज़, स्टार्च, ग्लाइकोजन।
Helpful Links
Carbohydrates are more than sugars – they’re the foundation of energy & structure in life.
