Chemical Bonding – Ionic Bonding
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, creating oppositely charged ions held together by electrostatic forces. Usually found between metals and non-metals.
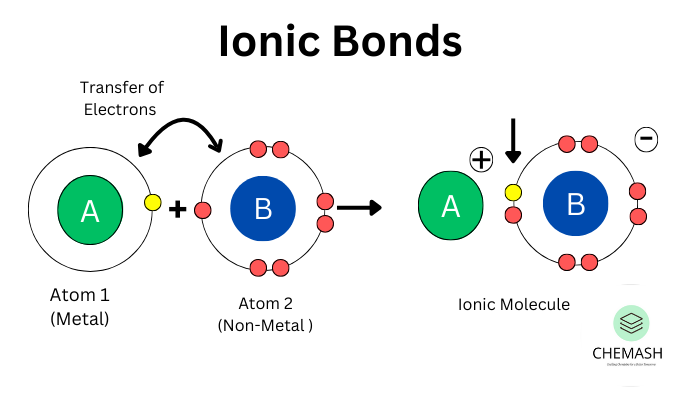
Formation of Ionic Bond
- Metals lose electrons → form cations.
- Non-metals gain electrons → form anions.
- Electrostatic attraction forms the bond.
Example: Sodium transfers one electron to chlorine → Na+ + Cl– → NaCl.
Characteristics of Ionic Compounds
- Crystalline solids with high melting & boiling points.
- Soluble in polar solvents (like water).
- Conduct electricity in molten/aqueous state, not in solid state.
- Hard and brittle in nature.
Factors Affecting Ionic Bond Strength
- Charge of ions: Higher charge → stronger bond (MgO > NaCl).
- Size of ions: Smaller ions → stronger bonds.
- Lattice energy: Higher lattice energy → more stable compound.
Examples of Ionic Compounds
| Compound | Formula | Constituent Ions |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium chloride | NaCl | Na+, Cl– |
| Magnesium oxide | MgO | Mg2+, O2– |
| Calcium fluoride | CaF2 | Ca2+, F– |
Lattice Energy
Lattice energy = energy released when one mole of ionic solid forms from gaseous ions.
- Higher lattice energy → stronger ionic bond → higher melting point.
- Increases with higher ionic charge and smaller ionic radii.
MCQ Quiz
- Ionic bond forms due to:
a) Sharing of electrons
b) Transfer of electrons
Answer: b) Transfer of electrons - Ionic compounds conduct electricity in:
a) Solid state
b) Molten/aqueous state
Answer: b) Molten/aqueous state - Which has higher lattice energy: NaCl or MgO?
Answer: MgO (higher charges, smaller size) - Typical property of ionic compounds?
High melting point & brittleness - Why soluble in water?
Because water stabilizes ions by ion-dipole interaction
FAQs on Ionic Bonding
Q1. What is an ionic bond?
A chemical bond formed due to transfer of electrons, creating cations and anions held by electrostatic forces.
Q2. Why are ionic compounds hard but brittle?
Strong ionic lattice makes them hard, but shifting ions bring like charges together, causing brittleness.
Q3. Why do ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten?
Because ions are free to move and carry charge in molten/aqueous state.
Q4. How does lattice energy affect stability?
Higher lattice energy means stronger ionic bonding and more stable compounds.
