Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes
Aldehydes are highly reactive organic compounds due to the presence of the –CHO group. The carbonyl carbon is electrophilic, making aldehydes excellent participants in a wide range of organic reactions.
1. Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
The electrophilic carbonyl carbon is attacked by nucleophiles, leading to various addition products:
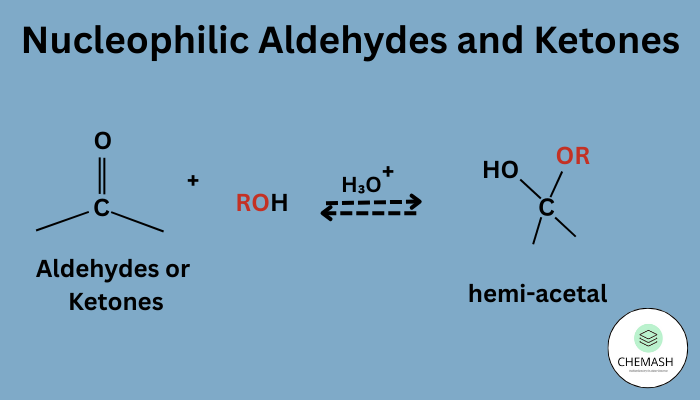
- With HCN: Forms cyanohydrins.
- With NaHSO₃: Forms bisulfite addition compounds.
- With NH₂OH, NH₂NH₂: Forms oximes and hydrazones.
2. Reduction Reactions
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols using:
- Hydrogen in the presence of Ni or Pt catalyst.
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH₄)
- Lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH₄)
3. Oxidation Reactions
Aldehydes are easily oxidized to carboxylic acids:
- With KMnO₄, K₂Cr₂O₇, or HNO₃.
- Tollens’ reagent: Gives silver mirror (Ag⁰).
- Fehling’s solution: Gives red precipitate of Cu₂O.
4. Aldol Condensation
Aldehydes with α-hydrogens undergo base-catalyzed condensation to form β-hydroxy aldehydes:
2 CH₃CHO → CH₃CH(OH)CH₂CHO → CH₃CH=CHCHO (on heating)
5. Cannizzaro Reaction
Aldehydes without α-hydrogen atoms undergo disproportionation in concentrated alkali:
2 HCHO + NaOH → HCOONa + CH₃OH
One molecule is oxidized, the other is reduced.
6. Reaction with Grignard Reagents
Aldehydes react with Grignard reagents to give secondary alcohols after hydrolysis:
RCHO + RMgX → RCH(OH)R'
Summary of Reactions
- Nucleophilic Addition: Forms cyanohydrins, oximes, etc.
- Reduction: Converts to primary alcohols.
- Oxidation: Easily forms carboxylic acids.
- Aldol Reaction: Forms β-hydroxy aldehydes.
- Cannizzaro Reaction: Disproportionation reaction.
- Grignard Reaction: Yields secondary alcohols.
Related Reading: Introduction to Aldehydes | Introduction to Ketones | External Reference: Aldehydes – Wikipedia
Quick MCQ Quiz
Q1: Which reagent gives a silver mirror test with aldehydes?
- A) Fehling’s solution
- B) Tollens’ reagent ✅
- C) KMnO₄
- D) NaBH₄
Q2: Cannizzaro reaction occurs in aldehydes:
- A) With α-hydrogens
- B) Without α-hydrogens ✅
- C) Only aromatic aldehydes
- D) Only aliphatic aldehydes
True/False Practice
- Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids. → True
- Grignard reaction with aldehydes gives primary alcohols. → False (it gives secondary alcohols)
- Aldol condensation occurs only in aldehydes without α-hydrogens. → False

Pingback: nomenclature-of-aldehydes-and-ketones