Chemical Reactions of Phenol
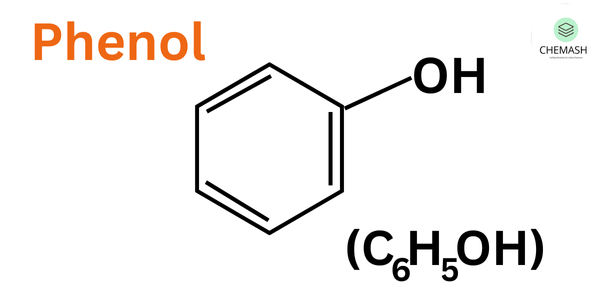
Phenol (C₆H₅OH) is an aromatic compound in which a hydroxyl group (–OH) is directly attached to a benzene ring. Due to resonance stabilization, phenol undergoes a wide range of chemical reactions, especially electrophilic substitution reactions.
1. Acidic Nature
Phenol is weakly acidic compared to alcohols but stronger than water because the phenoxide ion formed is resonance stabilized:
C₆H₅OH ⇌ C₆H₅O⁻ + H⁺
2. Reaction with Sodium
Phenol reacts with sodium metal liberating hydrogen gas:
2C₆H₅OH + 2Na → 2C₆H₅ONa + H₂↑
3. Reaction with Sodium Hydroxide
Phenol dissolves in NaOH to form sodium phenoxide:
C₆H₅OH + NaOH → C₆H₅ONa + H₂O
4. Electrophilic Substitution Reactions
- Nitration: With dilute HNO₃:
- With concentrated HNO₃:
- Halogenation: With Br₂ water:
5. Kolbe Reaction
Phenol reacts with CO₂ under pressure in alkaline medium to form salicylic acid:
C₆H₅ONa + CO₂ → o-Hydroxybenzoic acid (Salicylic acid)
6. Reimer–Tiemann Reaction
Phenol reacts with chloroform and NaOH to form salicylaldehyde:
C₆H₅OH + CHCl₃ + 3NaOH → o-Hydroxybenzaldehyde + 3NaCl + 2H₂O
7. Oxidation
Phenol oxidizes to benzoquinone in presence of strong oxidizing agents:
C₆H₅OH + [O] → C₆H₄O₂ (Benzoquinone) + H₂O
8. Reduction with Zinc
On heating with zinc dust, phenol reduces to benzene:
C₆H₅OH + Zn → C₆H₆ + ZnO
Summary Table
| Reaction | Reagents | Product |
|---|---|---|
| Acidic Reaction | Na / NaOH | Sodium phenoxide + H₂ |
| Nitration | HNO₃ (dil./conc.) | Nitrophenol / Picric acid |
| Halogenation | Br₂ water | 2,4,6-Tribromophenol |
| Kolbe Reaction | CO₂ + NaOH | Salicylic acid |
| Reimer–Tiemann | CHCl₃ + NaOH | Salicylaldehyde |
| Oxidation | Na₂Cr₂O₇ / [O] | Benzoquinone |
| Reduction | Zn (heat) | Benzene |
MCQ Quiz
- Phenol is more acidic than alcohol because:
a) Hydrogen bonding
b) Resonance stabilization of phenoxide ion ✅
c) Stronger O–H bond
d) None - The product of Kolbe reaction is:
a) Benzaldehyde
b) Picric acid
c) Salicylic acid ✅
d) Phenyl acetate - Phenol reacts with bromine water to give:
a) Benzaldehyde
b) 2,4,6-Tribromophenol ✅
c) Benzoquinone
d) Benzene
True/False Questions
- Phenol reacts with sodium to liberate hydrogen gas. ✅ True
- Kolbe reaction produces benzaldehyde. ❌ False (It produces salicylic acid)
- Phenol oxidizes to benzoquinone in presence of oxidizing agents. ✅ True
Related Links
🔗 Chemical Reactions of Alcohols (internal link)
🔗 Phenol – Wikipedia (external link)
🔗 Equilibrium and Free Energy (internal link)

Pingback: classification-of-alcohol
Pingback: Classification of Ethers
Pingback: interconversion-of-alcohols-phenols-and-ethers