Diazonium Salts (Aromatic Amines)
What are Diazonium Salts?
Diazonium salts are organic compounds containing the functional group –N2+. They are typically formed by the reaction of primary aromatic amines with nitrous acid (HNO2).
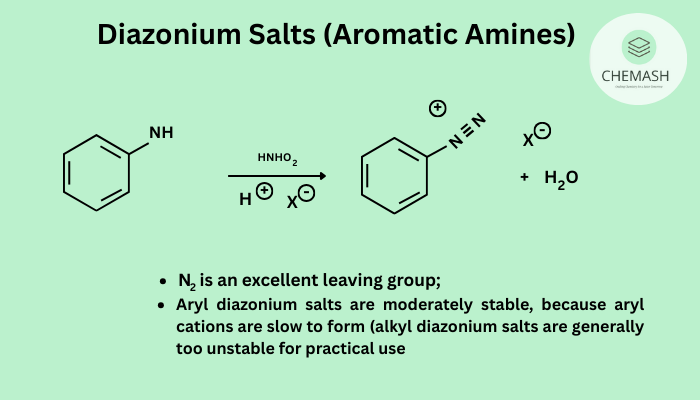
General Reaction (Diazotization)
Ar-NH2 + HNO2 + HCl → Ar-N2+Cl− + 2H2O
Note: Nitrous acid is generated in situ using sodium nitrite (NaNO2) and HCl. The reaction must be carried out below 5°C.
Key Properties
- Colorless crystalline solids.
- Stable only below 5°C.
- Highly reactive due to N2 being an excellent leaving group.
- Soluble in water and used immediately after preparation.
Reactions of Diazonium Salts
1. Substitution Reactions
- Sandmeyer Reaction: Ar-N2+Cl− + CuCl → Ar-Cl
- Gattermann Reaction: Ar-N2+Cl− + Cu/HCl → Ar-Cl
- Hydrolysis: Ar-N2+Cl− + H2O → Ar-OH + N2↑ + HCl
2. Coupling Reactions
Diazonium salts react with phenols or aromatic amines to form brightly colored azo dyes.
Ar-N2+ + Ar′-OH (or Ar′-NH2) → Ar-N=N-Ar′ (Azo dye)
Applications
- Used in synthesis of azo dyes (textiles, leather, inks).
- Preparation of halogenated aromatics via Sandmeyer/Gattermann reactions.
- Precursors for phenols and aromatic ethers.
- Applications in pharmaceuticals 💊, agrochemicals 🌾, organic semiconductors.
Practice & Quiz
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
- Diazonium salts are stable at:
- a) 25°C
- b) 0–5°C ✅
- c) 50°C
- d) 100°C
- The Sandmeyer reaction produces:
- a) Azo dye
- b) Phenol
- c) Halogenated aromatic ✅
- d) Carboxylic acid
Fill in the Blanks
1. Diazonium salts contain the functional group __________.
2. Coupling of diazonium salts with phenols forms __________ dyes.
True / False
1. Diazonium salts are stable at room temperature. (❌ False)
2. Nitrous acid is generated in situ using NaNO2 and HCl. (✅ True) 🔍 Precision tools in aromatic chemistry — Diazonium salts are short-lived, but powerful in synthesis.
