Classification of Alcohol
Alcohols are organic compounds containing one or more hydroxyl (–OH) groups attached to saturated (sp³ hybridized) carbon atoms. They can be classified in several ways based on their structure and composition.
I. Based on Number of Hydroxyl Groups
- Monohydric Alcohols: Contain one –OH group.
Example: Ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH) - Dihydric Alcohols (Glycols): Contain two –OH groups.
Example: Ethylene glycol (HO–CH₂–CH₂–OH) - Trihydric Alcohols: Contain three –OH groups.
Example: Glycerol (HO–CH₂–CH(OH)–CH₂OH) - Polyhydric Alcohols: Contain more than three –OH groups.
Example: Sorbitol
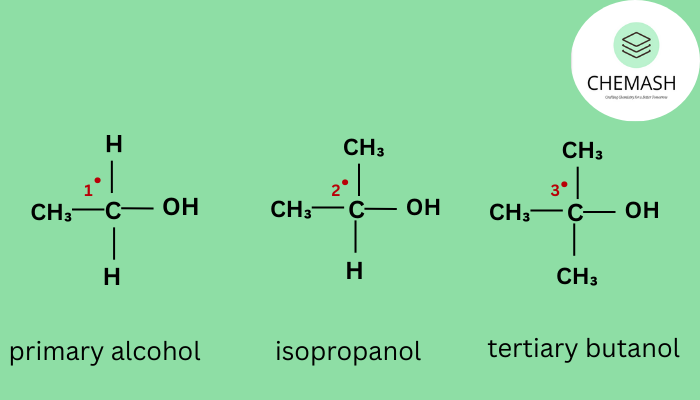
II. Based on the Nature of the Carbon Atom to which –OH is Attached
- Primary (1°) Alcohol: –OH attached to a carbon bonded to only one other carbon.
Example: Ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH) - Secondary (2°) Alcohol: –OH attached to a carbon bonded to two other carbons.
Example: Isopropanol (CH₃CHOHCH₃) - Tertiary (3°) Alcohol: –OH attached to a carbon bonded to three other carbons.
Example: Tert-butanol ((CH₃)₃COH)
III. Based on Saturation of Carbon Chain
- Saturated Alcohols: Contain only single bonds between carbon atoms.
Example: Propanol (CH₃CH₂CH₂OH) - Unsaturated Alcohols: Contain one or more double/triple bonds in the chain.
Example: Allyl alcohol (CH₂=CHCH₂OH)
IV. Based on Type of Carbon Chain
- Aliphatic Alcohols: Alcohols with open-chain (non-aromatic) structures.
Example: Methanol (CH₃OH) - Aromatic Alcohols: Alcohols where –OH is attached to a side chain on an aromatic ring.
Example: Benzyl alcohol (C₆H₅CH₂OH)
Summary Table
| Basis | Types | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Number of –OH Groups | Mono, Di, Tri, Polyhydric | Ethanol, Glycerol |
| Carbon Attachment | Primary, Secondary, Tertiary | Ethanol, Isopropanol, Tert-butanol |
| Saturation | Saturated, Unsaturated | Propanol, Allyl alcohol |
| Carbon Chain Type | Aliphatic, Aromatic | Methanol, Benzyl alcohol |
MCQ Quiz
- Which of the following is a dihydric alcohol?
a) Ethanol
b) Glycerol
c) Ethylene glycol ✅
d) Methanol - In tertiary alcohols, the –OH group is attached to:
a) One carbon
b) Two carbons
c) Three carbons ✅
d) Four carbons - Allyl alcohol is an example of:
a) Saturated alcohol
b) Unsaturated alcohol ✅
c) Polyhydric alcohol
d) Aromatic alcohol
True/False Questions
- Methanol is an aromatic alcohol. ❌ False
- Glycerol is a trihydric alcohol. ✅ True
- Aliphatic alcohols have open-chain structures. ✅ True
Related Links
🔗 Chemical Reactions of Alcohols (internal)
🔗 Chemical Reactions of Phenol (internal)
🔗 Alcohol – Wikipedia (external)

Pingback: ethers-explanation