Collision Theory
Collision Theory is a fundamental concept in chemical kinetics that explains the conditions under which chemical reactions occur. According to this theory, a chemical reaction happens only when the reacting particles—atoms, molecules, or ions—collide with each other. However, not all collisions result in a reaction. For a collision to be effective, two critical conditions must be met:
- The particles must have enough kinetic energy to overcome the activation energy barrier of the reaction.
- The particles must also be aligned in the correct orientation so that the necessary bonds can be broken and new bonds can form.
This means that chemical reactions depend not just on particles coming into contact, but also on how they collide and how energetic those collisions are. Collision Theory helps us understand why certain reactions occur faster than others, and what factors (like temperature, concentration, and catalysts) can influence the rate at which these effective collisions happen.
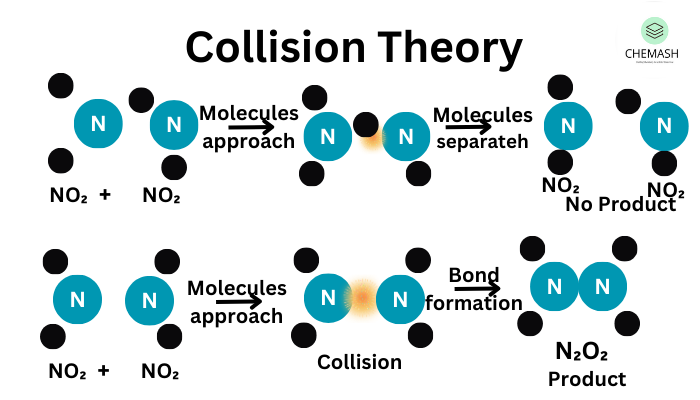
Key Principles of Collision Theory
- Particles Must Collide: Reactants need to come into contact to react. More collisions increase the chance of a reaction.
- Activation Energy (Ea): Only collisions with sufficient energy can break bonds and form new ones.
- Correct Orientation: Particles must be aligned properly during collisions, otherwise no reaction will occur.
Factors That Affect the Rate of Collision
| Factor | Effect on Reaction |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Increases particle movement and energy, leading to more successful collisions. |
| Concentration | More particles in the same space means more collisions per second. |
| Surface Area | Greater exposed area leads to more collisions (e.g., powdered solids). |
| Catalyst | Lowers the activation energy, making it easier for reactions to occur. |
Example Reaction: Hydrogen + Chlorine
When hydrogen gas (H2) reacts with chlorine gas (Cl2), they form hydrogen chloride (HCl). For this reaction to occur:
- The molecules must collide
- They must have enough energy
- They must be aligned correctly
