Diastereomers – Definition, Properties, Examples & Stereochemistry
Diastereomers are a type of stereoisomer that have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms but are not mirror images of each other. Unlike enantiomers, diastereomers differ in multiple physical and chemical properties.
Key Features of Diastereomers
- Not mirror images of each other
- Same connectivity of atoms but different spatial arrangement
- Have different physical properties (boiling point, melting point, solubility, density)
- May or may not rotate plane-polarized light, and rotation magnitudes differ
- Can have more than two stereoisomers in a group
Diastereomers occur only in molecules with two or more chiral centers.
Example: Tartaric Acid (HOOC-CH(OH)-CH(OH)-COOH)
Tartaric acid has two chiral centers and can exist as three stereoisomers:
- (R,R)-tartaric acid
- (S,S)-tartaric acid
- (R,S) or meso-tartaric acid
(R,R) and (S,S) are enantiomers of each other, while each of them is a diastereomer of the meso form.
Difference Between Enantiomers and Diastereomers
| Enantiomers | Diastereomers |
|---|---|
| Mirror images | Not mirror images |
| Same physical properties (except optical rotation) | Different physical & chemical properties |
| Always occur in pairs | May be 2 or more |
| Opposite optical rotation | No fixed relationship in optical rotation |
| Biological properties often differ | Biological properties differ strongly |
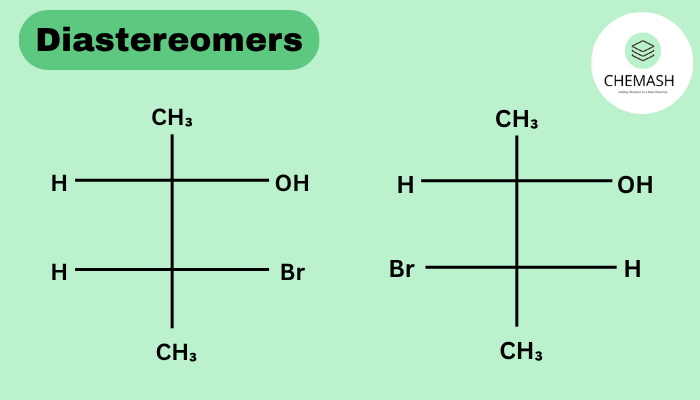
Meso Compounds & Diastereomer Relationship
A meso compound has multiple stereocenters but is achiral due to internal symmetry. A meso form is a diastereomer of the other stereoisomers.
Importance of Diastereomers in Real Life
- Crucial in drug design — different pharmacological actions
- Different smells, tastes, and biological responses
- Industrial separation easier due to different physical properties
FAQs
Q1: Can diastereomer be separated easily?
Yes — due to different physical properties, unlike enantiomers.
Q2: Can a molecule with one chiral center form diastereomer?
No — diastereomers require at least two chiral centers.
Q3: Are meso compounds diastereomer?
Yes — meso compounds are diastereomers of the other stereoisomers.
Quick Quiz
1. Diastereomers are:
- A) Superimposable mirror images
- B) Non-superimposable mirror images
- C) Stereoisomers that are not mirror images ✔️
2. Diastereomers have:
- A) Equal physical properties
- B) Different physical properties ✔️
- C) Opposite optical rotation only
Khan Academy – Stereochemistry
