Electrical & Magnetic Properties of Solids
Solid state chemistry not only deals with the structure of solids but also their electrical and magnetic behavior. These properties help classify materials into conductors, insulators, and semiconductors, or magnetic vs non-magnetic materials.
Electrical Properties
Solids conduct electricity differently depending on their internal structure:
- Conductors: Allow free flow of electrons (e.g., metals like copper, silver).
- Insulators: Do not conduct electricity (e.g., wood, glass).
- Semiconductors: Intermediate conductivity; used in electronics (e.g., silicon, germanium).
Band Theory Explanation
In solids, conduction depends on the availability of free electrons. According to band theory:
- Metals have overlapping valence and conduction bands.
- Insulators have a wide gap between bands.
- Semiconductors have a small band gap (~1 eV).
Magnetic Properties
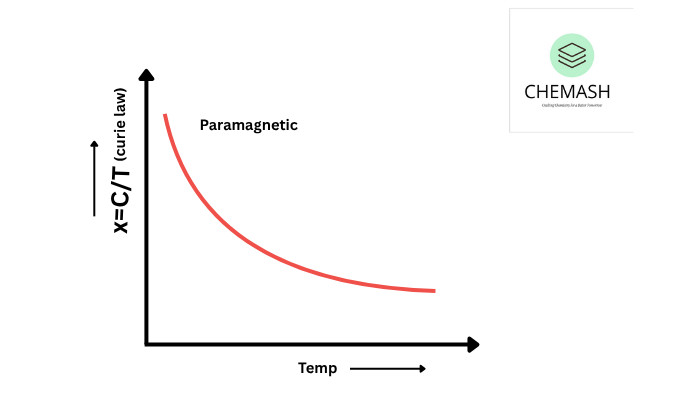
Solids react to magnetic fields based on electron arrangement. Types include:
- Diamagnetic: Weakly repelled by magnetic fields (e.g., Bi, Cu).
- Paramagnetic: Weakly attracted due to unpaired electrons (e.g., O₂, Fe³⁺).
- Ferromagnetic: Strongly attracted; retain magnetism (e.g., Fe, Co, Ni).
- Antiferromagnetic: Opposing spins cancel out (e.g., MnO).
- Ferrimagnetic: Unequal opposing spins, some net magnetism (e.g., Fe₃O₄).
Applications
- Conductors in electrical wiring
- Semiconductors in chips, transistors
- Ferromagnetic materials in hard disks and transformers
Conclusion
Understanding the electrical and magnetic behavior of solids is crucial in materials science and electronics. It enables the design of better circuits, magnetic devices, and advanced materials for the future.
Multiple Choice Questions on Electrical & Magnetic Properties
- Which of the following is a characteristic of conductors?
a) Full valence band
b) Overlapping conduction and valence bands
c) Wide band gap
d) Completely filled conduction band
Answer: b) Overlapping conduction and valence bands - Ferromagnetism is observed in:
a) Oxygen
b) Iron
c) Copper
d) Zinc
Answer: b) Iron - Intrinsic semiconductors are pure forms of:
a) Metals
b) Non-metals
c) Semiconductors
d) Superconductors
Answer: c) Semiconductors
True or False (with Explanation)
- True or False: Semiconductors conduct electricity only at absolute zero.
Answer: False
Explanation: Semiconductors conduct better at higher temperatures due to thermal excitation of electrons. - True or False: Paramagnetic substances are weakly attracted by magnetic fields.
Answer: True
Explanation: Paramagnetic substances have unpaired electrons that align with the magnetic field weakly.
Quick Quiz: Test Your Knowledge
Q: Which type of substance becomes a magnet when placed in a magnetic field and retains magnetism even after the field is removed?
- A) Paramagnetic
- B) Diamagnetic
- C) Ferromagnetic
- D) Antiferromagnetic
Correct Answer: C) Ferromagnetic
Explanation: Ferromagnetic substances like iron retain permanent magnetism due to domain alignment.
Also read: Density of Unit Cell | Introduction to Solid State
