Electrochemical Series Explained with Table, Examples & Quiz
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding the Electrochemical Series
- Standard Electrode Potential (E°)
- Example Table
- Significance
- Quiz
- FAQs
Introduction
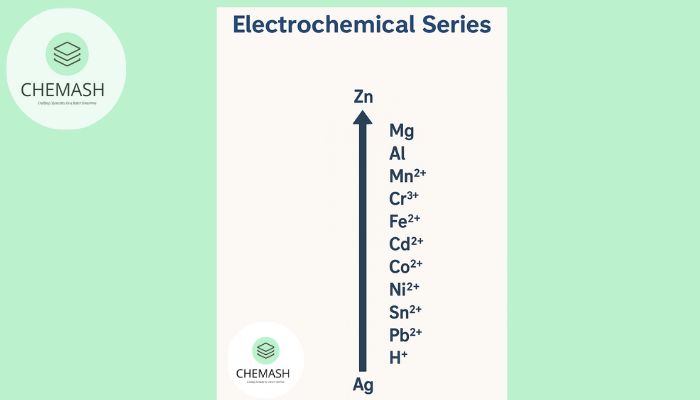
The Electrochemical Series, also called the activity series, arranges elements by their standard electrode potentials under standard conditions (25°C, 1 atm, 1 M). It reflects their ability to gain or lose electrons, indicating oxidizing and reducing power.
Understanding the Electrochemical Series
- Top elements → lose electrons easily → strong reducing agents.
- Bottom elements → gain electrons easily → strong oxidizing agents.
- Predicts redox direction & reactivity trends.
Standard Electrode Potential (E°)
– Measured against the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE).
– Positive E° → easier to be reduced.
– Negative E° → easier to be oxidized.
Example Electrochemical Series (Partial)
| Element / Ion | Half Reaction | E° (V) |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium (Li⁺/Li) | Li⁺ + e⁻ → Li | -3.04 |
| Zinc (Zn²⁺/Zn) | Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Zn | -0.76 |
| Hydrogen (H⁺/H₂) | 2H⁺ + 2e⁻ → H₂ | 0.00 |
| Copper (Cu²⁺/Cu) | Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu | +0.34 |
| Fluorine (F₂/F⁻) | F₂ + 2e⁻ → 2F⁻ | +2.87 |
Significance
- ✅ Predicts redox reaction feasibility.
- ✅ Explains corrosion tendency of metals.
- ✅ Guides electrode selection for cells.
- ✅ Shows oxidizing vs reducing strength.
Quiz:
- What does the electrochemical series represent?
- What is the E° of the hydrogen electrode?
- Which is a stronger reducing agent: lithium or copper?
- Why are metals higher more reactive?
- How does the series help in predicting displacement reactions?
Answers
- It ranks elements by standard electrode potentials.
- 0.00 V (reference).
- Lithium (more negative E°).
- They lose electrons more easily.
- A higher metal can displace a lower one.
FAQs
Q1: What is another name for the electrochemical series?
A: It is also called the activity series.
Q2: Why is hydrogen electrode set at 0 V?
A: To serve as a universal reference for measuring electrode potentials.
Q3: How does the series help in corrosion studies?
A: Metals higher in the series corrode more easily due to stronger reducing nature.
