Electrolysis in Electrochemistry
Using electrical energy to drive chemical changes that wouldn’t occur spontaneously.
What is Electrolysis?
Electrolysis is a redox process in which electrical energy is supplied externally to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. It is used to decompose substances, such as salts or water, into their elemental forms using direct electric current.
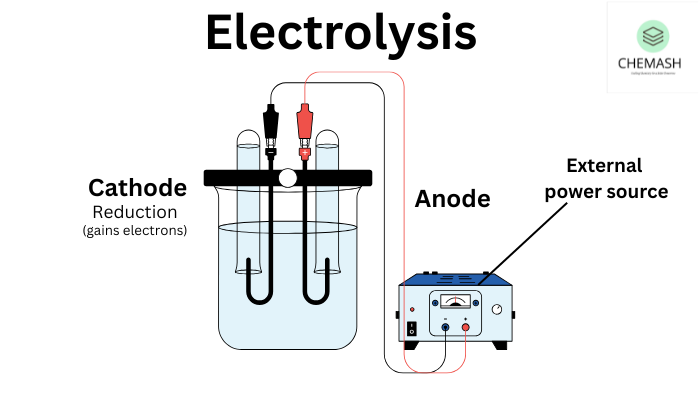
Basic Setup of Electrolysis
- Two electrodes:
- Cathode (−): Site of reduction (gains electrons)
- Anode (+): Site of oxidation (loses electrons)
- Electrolyte: Ionic compound (solution or molten) that allows current flow
- External power source: Provides the necessary energy for the redox reactions
Key Reactions
Example: Electrolysis of molten NaCl
Cathode (−): Na+ + e− → Na (reduction)
Anode (+): 2Cl− → Cl2 + 2e− (oxidation)
Overall: 2NaCl → 2Na + Cl2
Types of Electrolysis
- Molten salt electrolysis: e.g., NaCl, Al2O3
- Aqueous solution electrolysis: e.g., CuSO4, H2O
- Electroplating: Metal coating for corrosion protection and decoration
Factors Affecting Electrolysis
- Nature of the electrodes (inert vs. reactive)
- Concentration of the electrolyte
- Voltage supplied by the external source
- Standard electrode potentials of ions involved
Applications of Electrolysis
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Metal extraction | Obtaining metals like aluminum and sodium from their ores |
| Electroplating | Coating objects with metals like gold, silver, or nickel |
| Electrorefining | Purification of metals such as copper |
| Water electrolysis | Producing hydrogen and oxygen gases |
| Chlor-alkali process | Producing chlorine, hydrogen, and sodium hydroxide from brine |
Key Points to Remember
- Electrolysis requires external energy input to proceed
- The products depend on the type of electrolyte and electrodes
- Water may undergo electrolysis in aqueous systems, affecting the outcome
Quick Quiz: Test Your Understanding
- Which of the following is reduced at the cathode during the electrolysis of molten NaCl?
A) Na+ B) Cl− C) NaCl D) Cl2 - In electroplating, the object to be plated is connected to the:
A) Anode B) Cathode C) Electrolyte D) Battery terminal directly - What gas is produced at the anode during the electrolysis of water?
A) Hydrogen B) Oxygen C) Nitrogen D) Chlorine - Which factor does not significantly affect the electrolysis process?
A) Electrode material B) Electrolyte concentration C) Light intensity D) Voltage applied
Answers & Explanations:
- 1) A) Na+ – Sodium ions gain electrons (are reduced) to form metallic sodium at the cathode.
- 2) B) Cathode – The object to be plated is the cathode so that metal ions are reduced and deposited on it.
- 3) B) Oxygen – Water is oxidized at the anode to form oxygen gas and H+ ions.
- 4) C) Light intensity – Light does not affect electrolysis; only factors like voltage, electrodes, and concentration matter.
Electrolysis is vital in industrial chemistry, refining, and energy technology.
📝 MCQs on Electrolysis
1. What happens at the cathode during electrolysis?
- A. Oxidation
- B. Reduction ✅
- C. Electron loss
- D. No reaction
Explanation: The cathode is the negative electrode where reduction (gain of electrons) takes place during electrolysis.
2. In the electrolysis of molten NaCl, what is produced at the anode?
- A. Sodium metal
- B. Chlorine gas ✅
- C. Hydrogen gas
- D. Oxygen gas
Explanation: At the anode, Cl− ions are oxidized to chlorine gas: 2Cl− → Cl2 + 2e−.
3. Which of the following is NOT a factor affecting electrolysis?
- A. Type of electrode
- B. Concentration of electrolyte
- C. Type of solvent used ✅
- D. Applied voltage
Explanation: The solvent type matters in some chemistry, but electrolysis mainly depends on electrode material, electrolyte concentration, and voltage.
4. Why is direct current (DC) used in electrolysis instead of alternating current (AC)?
- A. AC is less powerful
- B. DC prevents heating
- C. DC provides a consistent direction of electron flow ✅
- D. AC cannot be used in liquids
Explanation: DC ensures one electrode remains cathode and the other anode, which is necessary for reduction and oxidation to occur at fixed positions.
5. What is the primary use of electrolysis in the chlor-alkali industry?
- A. Electroplating copper
- B. Producing chlorine, hydrogen, and sodium hydroxide ✅
- C. Refining iron
- D. Extracting aluminum
Explanation: The chlor-alkali process uses electrolysis of brine (NaCl solution) to produce chlorine gas, hydrogen gas, and NaOH solution.
Also read: Types of Electrochemical Cells
Learn more about: Redox Reactions
Understand metal purification in detail: Electrorefining of Metals
Learn more from the official chemistry source: Britannica: Electrolysis
Explore electrolysis in energy research: U.S. Department of Energy – Electrolysis for Hydrogen
Basic concept explained: Khan Academy – Electrolysis Overview
Drag and Drop Quiz – Match the Electrolysis Terms
Drag the correct definition to match each term:
Terms
Cathode
Anode
Electrolyte
External Power
Definitions
Site of reduction (gains electrons)
Site of oxidation (loses electrons)
Ionic solution that allows current flow
Supplies electrical energy for reactions
✅ Tip: You can use WordPress plugins like H5P or WP Quiz to make this fully interactive!
True or False – Electrolysis Facts
- Electrolysis occurs spontaneously without energy input.
❌ False – It requires external electrical energy to proceed. - Reduction always takes place at the cathode during electrolysis.
✅ True – The cathode is the site where reduction (gain of electrons) occurs. - Chlorine gas is produced at the cathode during NaCl electrolysis.
❌ False – It’s produced at the anode. - Electroplating is an application of electrolysis.
✅ True – It is widely used for coating metals. - Electrolytes must be solid to conduct electricity.
❌ False – They must be molten or in solution form.
True or False – इलेक्ट्रोलिसिस तथ्य (Electrolysis Facts)
- Electrolysis occurs spontaneously without energy input.
इलेक्ट्रोलिसिस बिना ऊर्जा आपूर्ति के स्वयं होता है।
❌ False / असत्य – यह प्रतिक्रिया को चलाने के लिए बाहरी विद्युत ऊर्जा की आवश्यकता होती है। - Reduction always takes place at the cathode during electrolysis.
इलेक्ट्रोलिसिस में कैथोड पर हमेशा अपचयन (reduction) होता है।
✅ True / सत्य – कैथोड पर इलेक्ट्रॉन प्राप्त होते हैं, जिससे अपचयन होता है। - Chlorine gas is produced at the cathode during NaCl electrolysis.
NaCl के इलेक्ट्रोलिसिस में क्लोरीन गैस कैथोड पर बनती है।
❌ False / असत्य – क्लोरीन गैस एनोड (anode) पर बनती है। - Electroplating is an application of electrolysis.
इलेक्ट्रोप्लेटिंग इलेक्ट्रोलिसिस का एक अनुप्रयोग है।
✅ True / सत्य – यह धातुओं की कोटिंग के लिए प्रयोग होती है। - Electrolytes must be solid to conduct electricity.
विद्युत प्रवाह के लिए इलेक्ट्रोलाइट ठोस होना चाहिए।
❌ False / असत्य – इलेक्ट्रोलाइट को द्रव या विलयन में होना चाहिए ताकि आयन गतिशील हों।

Pingback: Introduction to Electrochemistry -