What is Electronic Configuration?
Electronic configuration refers to the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom. It determines chemical behavior, reactivity, bonding and periodic-table position. Electrons fill orbitals according to quantum rules and energy order.
Rules for Writing Electronic Configuration
- Aufbau Principle: Fill lowest energy orbitals first (1s → 2s → 2p → 3s …).
- Pauli Exclusion Principle: Max two electrons per orbital with opposite spins.
- Hund’s Rule: Single-occupy degenerate orbitals before pairing.
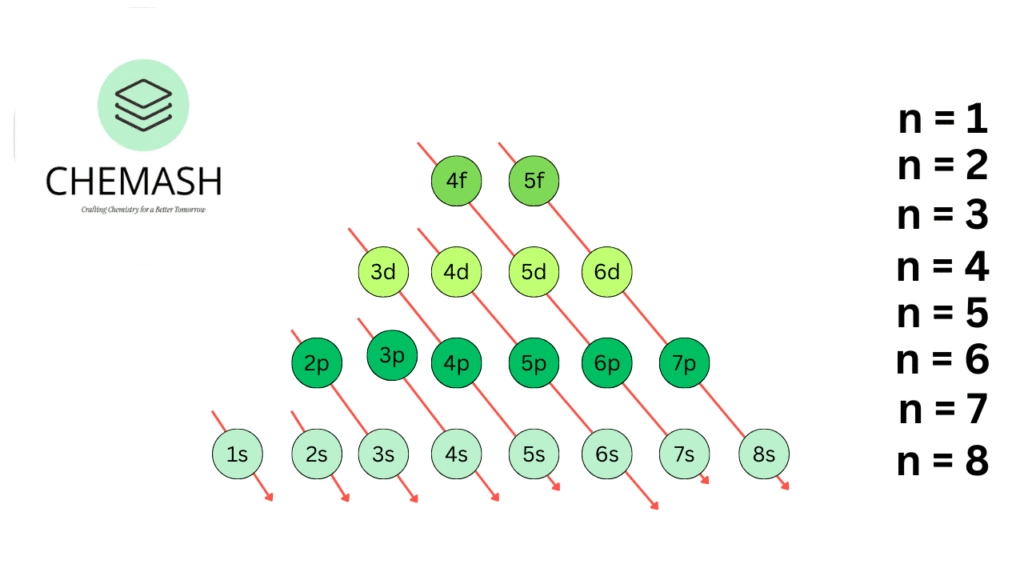
Aufbau Diagram — order of orbital filling
Notation & Examples
Use subshell labels with superscripts to show electron counts. Examples: Hydrogen: 1s1, Oxygen: 1s2 2s2 2p4, Sodium: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1.
Electronic Configuration of First 20 Elements
| Element | Symbol | Z | Electronic Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H | 1 | 1s1 |
| Helium | He | 2 | 1s2 |
| Lithium | Li | 3 | 1s2 2s1 |
| Beryllium | Be | 4 | 1s2 2s2 |
| Boron | B | 5 | 1s2 2s2 2p1 |
| Carbon | C | 6 | 1s2 2s2 2p2 |
| Nitrogen | N | 7 | 1s2 2s2 2p3 |
| Oxygen | O | 8 | 1s2 2s2 2p4 |
| Fluorine | F | 9 | 1s2 2s2 2p5 |
| Neon | Ne | 10 | 1s2 2s2 2p6 |
| Sodium | Na | 11 | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 |
| Magnesium | Mg | 12 | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 |
| Aluminium | Al | 13 | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 |
| Silicon | Si | 14 | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 |
| Phosphorus | P | 15 | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3 |
| Sulfur | S | 16 | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 |
| Chlorine | Cl | 17 | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5 |
| Argon | Ar | 18 | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 |
| Potassium | K | 19 | 1s2 … 4s1 |
| Calcium | Ca | 20 | 1s2 … 4s2 |
Significance
- Explains chemical bonding and valency
- Determines position in the periodic table
- Predicts physical and chemical properties
- Identifies reactivity and inert behavior
(MCQ)
Q1: What is the electronic configuration of Oxygen?
A) 1s2 2s2 2p6
B) 1s2 2s2 2p4
C) 1s2 2s1 2p5
D) 1s2 2s2 2p5
Answer & Explanation
Correct: B — Oxygen has 8 electrons; the filling order gives 1s² 2s² 2p⁴. (2 in 1s, 2 in 2s, remaining 4 in 2p)
Q2: Which rule explains why electrons occupy separate orbitals before pairing?
A) Aufbau Principle
B) Pauli Exclusion Principle
C) Hund’s Rule
D) Dalton’s Law
Answer & Explanation
Correct: C — Hund’s Rule: electrons maximize multiplicity by occupying degenerate orbitals singly before pairing.
Q3: What is the electronic configuration of Sodium (Na)?
A) 1s2 2s2 2p6
B) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
C) 1s2 2s2 2p4 3s2
D) 1s2 2s2 3p5
Answer & Explanation
Correct: B — Sodium has 11 electrons; core 1s²2s²2p⁶ then 3s¹.
Further reading: Atomic Structure •
Wikipedia — Electronic configuration.

Pingback: Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom - CHEMASH
Pingback: General Characteristics of Quantum Numbers - CHEMASH
Pingback: Group 17: Halogens - CHEMASH
Pingback: Group 18: Noble Gases - CHEMASH