Emulsion: Definition, Types, Properties, and Applications
Emulsion refers to a mixture where one liquid disperses into another liquid in the form of small droplets. Typically, these two liquids remain immiscible under normal conditions. For example, oil and water create an emulsion when mixed with an emulsifying agent.
Types of Emulsion
- Oil-in-Water (O/W): Oil droplets disperse in water. For instance, milk falls into this category.
- Water-in-Oil (W/O): Water droplets disperse in oil. For example, butter forms this type.
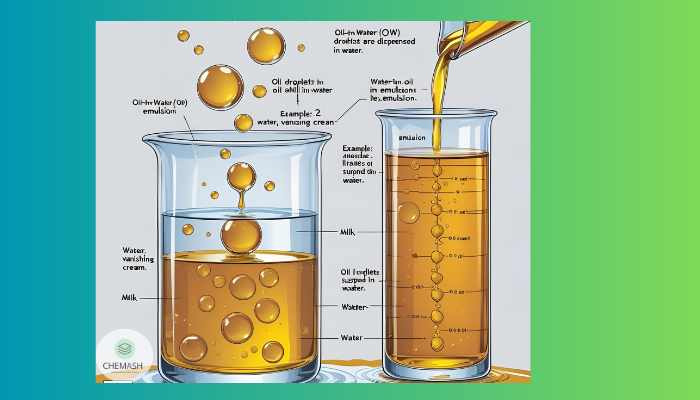
Properties of Emulsion
- Emulsions appear cloudy or opaque due to light scattering by dispersed particles.
- They require emulsifying agents for stability.
- The droplet size usually ranges from 0.1 to 10 micrometers.
Applications of Emulsion
- Food industry: Used in products like milk, mayonnaise, and ice cream.
- Pharmaceuticals: Helps deliver drugs in liquid forms.
- Cosmetics: Found in creams, lotions, and shampoos.
- Paints: Emulsion paints spread easily and dry quickly.
Quiz: Test Your Understanding
MCQs
- Which of the following is an oil-in-water emulsion?
A) Butter
B) Milk
C) Cold cream
D) Margarine
Answer: B) Milk - What is the typical droplet size in an emulsion?
A) 1–100 nm
B) 0.1–10 µm
C) 1–10 cm
D) None of these
Answer: B) 0.1–10 µm - Which industry uses emulsions in lotions and creams?
A) Textile
B) Cosmetics
C) Automobile
D) Agriculture
Answer: B) Cosmetics - Which component stabilizes an emulsion?
A) Surfactant
B) Salt
C) Sugar
D) Water
Answer: A) Surfactant - What type of emulsion is butter?
A) Oil-in-water
B) Water-in-oil
C) Gas-in-liquid
D) None
Answer: B) Water-in-oil
True / False
- Milk is an example of water-in-oil emulsion. — ❌ False
- Emulsions need emulsifying agents for stability. — ✅ True
- All emulsions are transparent. — ❌ False
- Paints can be emulsions. — ✅ True
- Oil and water mix easily without agents. — ❌ False
