Enzymes & Metabolism – CHEMASH Biology
Enzymes & Metabolism are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms. Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions occurring inside cells. This topic is extremely important for Class 11 Biology, NEET 2026, Boards and competitive exams.
Related CHEMASH topics: Biomolecules Simplified | Cell Organelles & Functions
Table of Contents
- What are Enzymes?
- Mechanism of Enzyme Action
- Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
- Types of Enzymes
- Metabolism
- Anabolism vs Catabolism
- Comparison Table
- MCQs with Explanation
- FAQs
What are Enzymes?
Enzymes are mostly proteins that act as catalysts and increase the rate of biochemical reactions without being consumed. They lower activation energy and make reactions faster.
- Protein in nature (except ribozymes)
- Highly specific
- Reusable
- Work best at optimum temperature & pH
Example: Amylase breaks down starch into sugars.
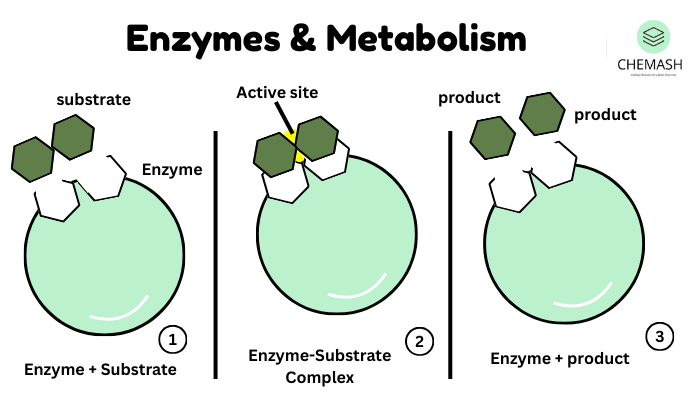
Mechanism of Enzyme Action
Enzymes work through the Lock and Key Model or Induced Fit Model.
- Substrate binds to active site
- Enzyme-substrate complex forms
- Product forms and released
- Enzyme remains unchanged
Reaction: Enzyme + Substrate → ES Complex → Product + Enzyme
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
- Temperature: High temperature denatures enzymes.
- pH: Each enzyme has optimum pH.
- Substrate concentration: Rate increases up to saturation.
- Enzyme concentration: More enzymes = faster reaction.
- Inhibitors: Reduce enzyme activity.
Types of Enzymes
- Oxidoreductases – Oxidation reactions
- Transferases – Transfer functional groups
- Hydrolases – Hydrolysis reactions
- Lyases – Remove groups without hydrolysis
- Isomerases – Rearrangement reactions
- Ligases – Join molecules
What is Metabolism?
Metabolism is the sum total of all biochemical reactions occurring in living organisms. It includes both building-up and breakdown reactions.
Anabolism vs Catabolism
| Process | Meaning | Energy | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anabolism | Building complex molecules | Requires energy | Protein synthesis |
| Catabolism | Breaking molecules | Releases energy | Respiration |
Quick Comparison
| Term | Main Function |
|---|---|
| Enzymes | Speed up reactions |
| Metabolism | Total chemical reactions |
| Anabolism | Build molecules |
| Catabolism | Break molecules |
MCQs with Explanation (NEET 2026)
1. Enzymes are mainly composed of:
Answer: Proteins
Explanation: Most enzymes are protein molecules.
2. Breakdown reactions are called:
Answer: Catabolism
Explanation: Catabolic reactions release energy.
3. Site where substrate binds enzyme?
Answer: Active Site
Explanation: Substrate fits specifically into active site.
FAQs
Q1. Do enzymes get consumed during reaction?
A: No, enzymes remain unchanged.
Q2. Why are enzymes specific?
A: Because active site shape matches only specific substrates.
Official reference: NCERT Biology Textbook
Learn with CHEMASH
CHEMASH provides affordable tuition for Biology, Chemistry and Physics. Experienced teachers, exam-focused learning, problem solving sessions and trusted guidance for 2026 exams. Join CHEMASH Tuition

Pingback: Biology MCQ Quiz | Class 9, 11 & NEET 2026 – CHEMASH