Eutrophication and Its Impact
Understanding the causes, processes, and environmental consequences of eutrophication.
Contents
3. Environmental & Ecological Impact
4. Quiz & MCQs (with explanations)
7. हिन्दी अनुभाग (Hindi section)
What is Eutrophication?
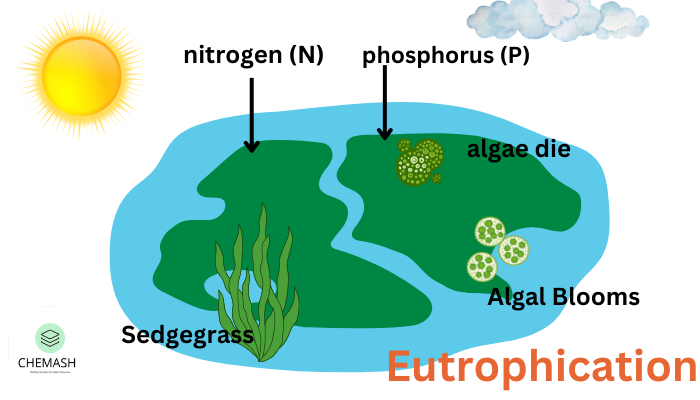
Eutrophication is a process where water bodies become excessively enriched with nutrients, primarily nitrogen and phosphorus, often due to runoff containing fertilizers, sewage, and detergents. This nutrient overload promotes the rapid growth of algae and aquatic plants.
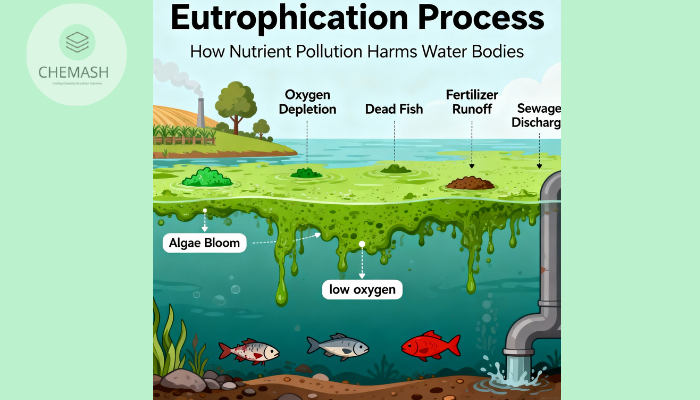
Process of Eutrophication
The nutrient influx causes algal blooms that block sunlight from reaching submerged plants, disrupting photosynthesis. When algae die, bacterial decomposition consumes dissolved oxygen, leading to hypoxia (low oxygen levels) and sometimes anoxia (no oxygen), which harms aquatic life.
Environmental and Ecological Impact
- Reduction in biodiversity due to oxygen depletion and habitat alteration.
- Fish kills and decline in aquatic fauna populations.
- Disruption of food chains and aquatic ecosystems.
- Water quality deterioration — unsafe for consumption and recreation.
- Economic losses in fisheries and tourism industries.
Quiz – Eutrophication and Its Impact
Select an answer for each multiple choice question and then click Check Answers to reveal explanations.
- 1. Which nutrients primarily cause eutrophication?
- Carbon and hydrogen
- Nitrogen and phosphorus
- Oxygen and hydrogen
- Sodium and potassium
- 2. What happens to oxygen levels during eutrophication?
- Increase
- Remain constant
- Decrease leading to hypoxia
- Fluctuate randomly
- 3. One major consequence of eutrophication is:
- Increased fish population
- Improved water clarity
- Fish kills due to oxygen depletion
- Enhanced recreational water use
- 4. Eutrophication can be controlled by:
- Increasing fertilizer runoff
- Reducing nutrient discharge into water bodies
- Dumping more sewage
- Encouraging algal blooms
Check AnswersShow ExplanationsReset
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can eutrophication be reversed?
A: In many cases, yes — by reducing nutrient inputs and through active remediation (e.g., aeration, dredging, constructed wetlands). Recovery can take months to years depending on severity.
Q: Are algal blooms always toxic?
A: No — some algal blooms are non-toxic, but harmful algal blooms (HABs) produce toxins that pose risks to humans and animals.
Q: How do farmers reduce nutrient runoff?
A: Methods include precision fertilizer application, buffer strips, cover crops, and controlled drainage practices.
- External (authoritative): US EPA — Nutrient Pollution
- External (health): World Health Organization
यू्ट्रोफिकेशन और इसका प्रभाव
पोषक तत्त्वों (मुख्यतः नाइट्रोजन और फॉस्फोरस) की अधिकता से जल निकायों में होने वाली प्रक्रिया, जिससे चारा पोषण बढ़ता है और पर्यावरण पर नकारात्मक प्रभाव पड़ता है।
यू्ट्रोफिकेशन क्या है?
यू्ट्रोफिकेशन तब होता है जब नदियों, झीलों या अन्य जल निकायों में नाइट्रोजन और फॉस्फोरस जैसे पोषक तत्त्वों की मात्रा असाधारण रूप से बढ़ जाती है। यह उर्वरक, सीवेज या डिटर्जेंट के बहाव की वजह से हो सकता है।
प्रक्रिया
इन पोषक तत्त्वों से शैवाल तेजी से बढ़ते हैं और पानी में घुलनशील ऑक्सीजन की मात्रा घट जाती है, जिससे हाइपोक्सिया (ऑक्सीजन की कमी) हो जाती है और मछलियाँ तथा अन्य जलीय जीव प्रभावित होते हैं।
प्रश्नोत्तरी (MCQ)
- प्रश्न: यू्ट्रोफिकेशन के मुख्य कारण कौन से हैं?
उत्तर: नाइट्रोजन और फॉस्फोरस। - प्रश्न: यू्ट्रोफिकेशन के समय ऑक्सीजन का क्या होता है?
उत्तर: ऑक्सीजन घट जाती है (हाइपोक्सिया)। - प्रश्न: यू्ट्रोफिकेशन को नियंत्रित करने का एक तरीका क्या है?
उत्तर: जल निकायों में पोषक तत्त्वों के निकास को कम करना।
© CHEMASH — Educational resources for chemistry and environment.
