Galvanic Cells (Voltaic Cells)
A Galvanic Cell, also known as a Voltaic Cell, is an electrochemical cell that converts chemical energy into electrical energy through spontaneous redox reactions. This process powers devices and forms the basis of modern batteries. Galvanic Cells (Voltaic Cells)
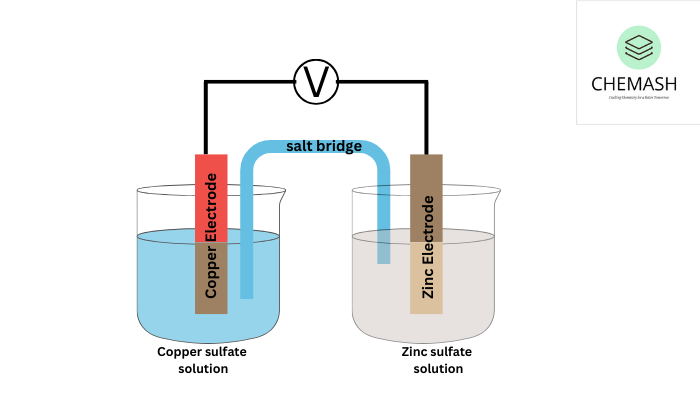
Basic Components of a Galvanic Cell
- Two Electrodes: Metals acting as oxidation (anode) and reduction (cathode) sites.
- Electrolyte Solutions: Ionic solutions enabling ion exchange.
- Salt Bridge: Maintains charge balance between half-cells.
Working Principle
In a galvanic cell:
- Oxidation occurs at the anode.
- Reduction occurs at the cathode.
Electrons flow from anode → cathode via wire, while ions move through the salt bridge. Learn more about Electrolytic Cells.
Example: Daniell Cell
- Anode (Zinc): Zn → Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻
- Cathode (Copper): Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu
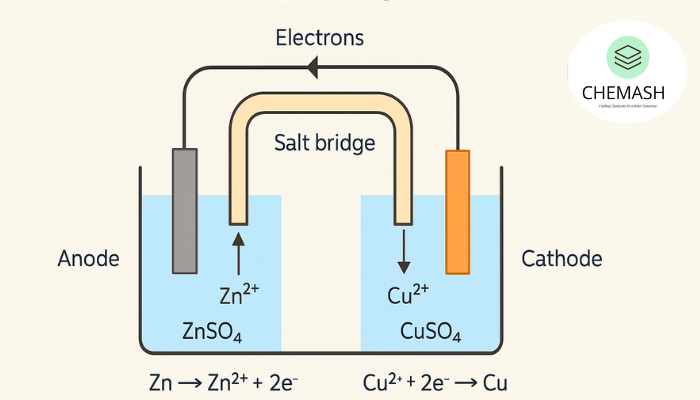
This spontaneous redox reaction generates electricity.
Galvanic Cell vs Electrolytic Cell
| Aspect | Galvanic Cell | Electrolytic Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Conversion | Chemical → Electrical | Electrical → Chemical |
| Reaction Type | Spontaneous | Non-spontaneous |
| Electrode Polarity | Anode (–), Cathode (+) | Anode (+), Cathode (–) |
| Electron Flow | Anode → Cathode | External Source → Cathode |
| Applications | Batteries, Fuel Cells | Electroplating, Electrolysis |
Quiz: Check Your Understanding
- What is the primary function of a galvanic cell?
- Which electrode undergoes oxidation?
- What role does the salt bridge play?
- Give one example of a galvanic cell.
- In which direction do electrons flow?
Answers with Explanations
- To convert chemical energy → electrical energy (spontaneous redox).
- Anode (site of oxidation).
- Maintains charge neutrality via ion exchange.
- Daniell Cell (Zn–Cu cell).
- Electrons flow externally from anode → cathode.
MCQs (with Answers)
- In a galvanic cell, the anode is:
✅ a) Negative electrode - The salt bridge is used to:
✅ c) Maintain charge balance - Which of the following is NOT a galvanic cell?
✅ b) Electrolytic cell - In the Daniell cell, copper undergoes:
✅ b) Reduction - Electron flow is from:
✅ b) Anode → Cathode
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is a galvanic cell?
A galvanic cell is an electrochemical cell that converts chemical energy into electrical energy via spontaneous redox reactions.
Q2: How does a salt bridge work?
It allows ions to flow between half-cells to maintain electrical neutrality, preventing charge buildup.
Q3: What is the difference between galvanic and electrolytic cells?
Galvanic cells operate spontaneously to produce current, while electrolytic cells require an external power source to drive non-spontaneous reactions.

Pingback: Electrochemical Cells - CHEMASH
Pingback: Introduction to Electrochemistry - CHEMASH