Greenhouse Gases and Global Warming
Major Greenhouse Gases
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Released from fossil fuel burning, deforestation, and respiration.
- Methane (CH₄): Emitted from livestock, rice paddies, and landfills.
- Nitrous Oxide (N₂O): Produced from agricultural fertilizers and industry.
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs): Synthetic compounds that damage the ozone layer.
- Water Vapor (H₂O): The most abundant GHG, enhancing the natural greenhouse effect.
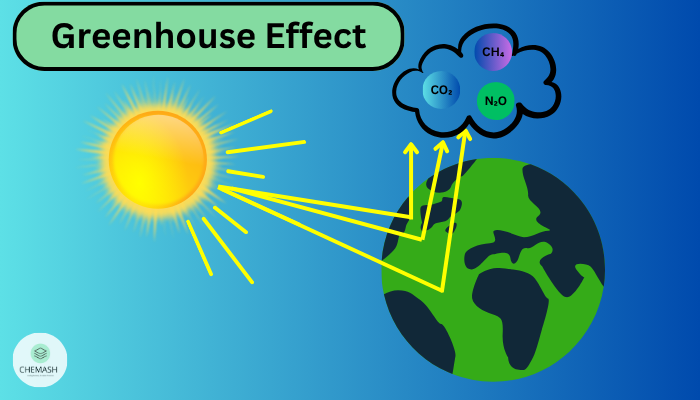
Mechanism of Global Warming
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) trap heat from the sun, maintaining Earth’s temperature but also contributing to global warming when present in excess.
Greenhouse gases absorb infrared radiation emitted by Earth’s surface, trapping heat — this is called the greenhouse effect. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), human-induced emissions have intensified this process, leading to rising temperatures.

- Solar radiation reaches Earth and warms the surface.
- The Earth emits heat as infrared radiation.
- GHGs absorb and re-emit part of this heat.
- Excess GHGs trap more heat, raising global temperatures.

Effects of Global Warming
- Rising sea levels from melting glaciers and ice caps.
- More frequent extreme weather events like storms and droughts.
- Ecosystem disruption and biodiversity loss.
- Reduced agricultural productivity.
- Increased health risks like heat strokes and vector-borne diseases (WHO Climate Impact).
Quiz – Greenhouse Gases & Global Warming
- Which is the most abundant greenhouse gas?
a) CO₂
b) CH₄
c) H₂O
d) N₂O
Answer: c) Water vapor
Explanation: Water vapor is the most naturally abundant GHG. - What activity contributes most to CO₂ increase?
a) Deforestation
b) Fossil fuel burning
c) Agriculture
d) Transport
Answer: b)
Explanation: Burning fossil fuels releases large CO₂ volumes. - Which gas traps heat effectively but is less abundant?
a) CH₄
b) N₂
c) O₂
d) Ar
Answer: a) Methane
Explanation: Methane traps more heat per molecule than CO₂. - Enhanced greenhouse effect leads to:
a) Cooling
b) Acid rain
c) Global warming
d) Ozone recovery
Answer: c)
Explanation: Extra heat trapped by GHGs causes global warming.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What causes greenhouse gases to increase?
Human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrialization increase GHG levels.
Q2. What are the main effects of global warming?
It causes climate change, melting ice caps, rising sea levels, and health problems due to heat.
Q3. Which organizations monitor global warming?
Organizations like IPCC and NASA Climate Division monitor and analyze climate trends.
Q4. How can individuals help reduce greenhouse gases?
By using renewable energy, reducing waste, planting trees, and supporting sustainable practices.
Up Next: Control Measures and Air Quality Index (AQI)
