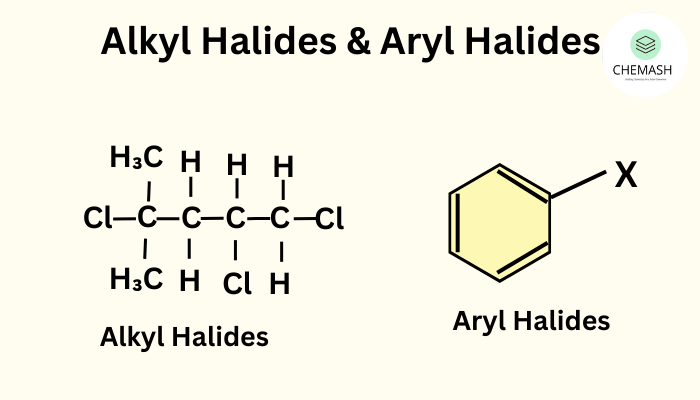
Introduction
Haloalkanes, also known as alkyl halides, are organic compounds where one or more hydrogen atoms in an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms (F, Cl, Br, or I). General formula: R–X.
Classification
- Primary Haloalkanes: Halogen attached to a primary carbon (1°).
- Secondary Haloalkanes: Halogen attached to a secondary carbon (2°).
- Tertiary Haloalkanes: Halogen attached to a tertiary carbon (3°).
Methods of Preparation
- From Alkanes: Free radical halogenation with UV light.
- From Alcohols: Reaction with HX, PCl₅, or SOCl₂.
- From Alkenes: Addition of HX or halogenation.
Physical Properties
- Colorless liquids or gases.
- Higher boiling points than alkanes.
- Soluble in organic solvents but insoluble in water.
Chemical Properties
1. Nucleophilic Substitution (SN1 & SN2)
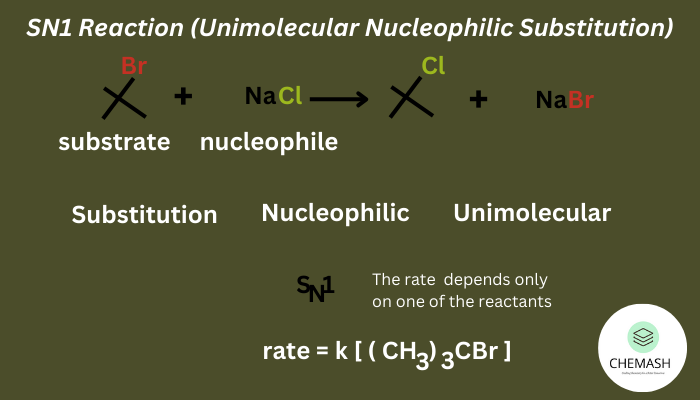
Halogen replaced by nucleophile:
- SN2: One-step, favored by 1° haloalkanes, inversion of configuration.
- SN1: Two-step, favored by 3° haloalkanes, carbocation intermediate, racemization.
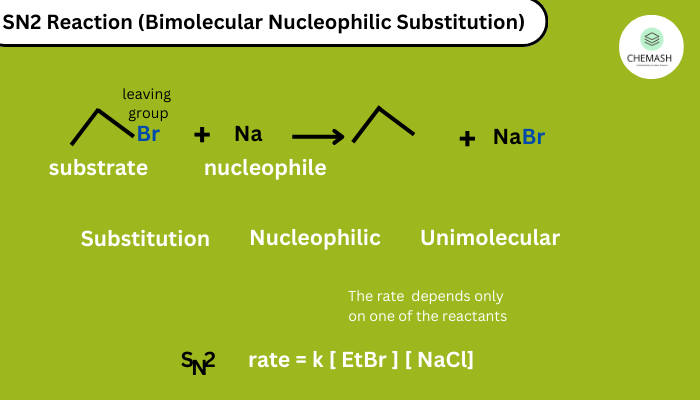
2. Elimination Reactions (E1 & E2)
Formation of alkenes:
- E2: One-step, strong base, 1°/2° haloalkanes.
- E1: Two-step, carbocation intermediate, 3° haloalkanes.
3. Reaction with Metals
- Grignard reagent: R–X + Mg → R–MgX
- Wurtz reaction: 2 R–X + 2 Na → R–R + 2 NaX
Uses
- Solvents in organic synthesis.
- Pharmaceutical & agrochemical intermediates.
- Refrigerants & fire extinguishers.
Environmental Impact
Many haloalkanes deplete ozone and contribute to global warming. Controlled under international treaties (e.g., Montreal Protocol).
Summary: Haloalkanes are versatile compounds, mainly undergoing substitution & elimination reactions. Their reactivity depends on alkyl structure and halogen type.
FAQs
Q1. Why do haloalkanes have higher boiling points than alkanes?
Because of stronger dipole–dipole interactions due to polar C–X bond.
Q2. Which haloalkanes undergo SN1 reactions faster?
Tertiary haloalkanes, due to stable carbocation formation.
Q3. Are haloalkanes soluble in water?
No, they are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
Practice Quiz
MCQ 1: Which reagent is used for preparing haloalkanes from alcohols?
Ans: PCl₅ or SOCl₂ ✅
True/False: Haloalkanes are generally insoluble in water.
True ✅
Fill in the blank: In SN2 reactions, configuration is ______.
Ans: Inverted ✅
Matching:
| Reaction | Feature |
|---|---|
| SN1 | Carbocation intermediate |
| SN2 | One-step mechanism |
| E1 | Two-step elimination |
| E2 | Strong base required |
हिंदी नोट्स
हैलोअल्केन (Alkyl Halides): ये वे यौगिक हैं जिनमें अल्केन के हाइड्रोजन परमाणु को हैलोजन (F, Cl, Br, I) से प्रतिस्थापित कर दिया जाता है।
- SN1: दो-चरणीय अभिक्रिया, तृतीयक हैलोअल्केन में अधिक होती है।
- SN2: एक-चरणीय अभिक्रिया, प्राथमिक हैलोअल्केन में होती है।
- उपयोग: औषधि उद्योग, विलायक, रेफ्रिजरेंट।
Next Topic: Haloarenes (Aryl Halides) | External Reference: Wikipedia: Haloalkanes
