Solubility Product (Ksp) in Chemical Equilibrium
Solubility Product (Ksp) is a special equilibrium constant that applies to sparingly soluble salts. It helps predict solubility, precipitation, and ion concentration in solutions.
Concept of Solubility Product
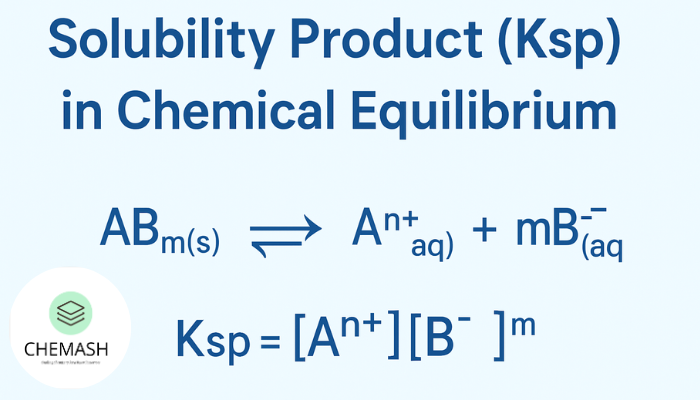
When a salt dissolves, it establishes a dynamic equilibrium between solid and ions:
ABm(s) ⇌ An+(aq) + mBz-(aq)
At equilibrium, the solubility product is:
Ksp = [An+] × [Bz-]m
Example: Silver Chloride (AgCl)
Dissolution of AgCl:
AgCl(s) ⇌ Ag+(aq) + Cl–(aq)
Ksp = [Ag+] × [Cl–]
Relation Between Solubility and Ksp
If molar solubility = s:
- [An+] = s
- [Bz-] = m × s
Thus, Ksp = s × (ms)m = mm sm+1
Factors Affecting Solubility
- Temperature: Higher T increases solubility for most salts.
- Common Ion Effect: Common ions decrease solubility.
- pH: Affects salts with acidic/basic ions.
Applications of Ksp
- Predicting precipitation in ionic reactions.
- Calculating solubility of sparingly soluble salts.
- Qualitative and quantitative analysis in chemistry labs.
- Water treatment and pharmaceutical formulations.
Summary
- Ksp = product of equilibrium ion concentrations.
- Relates solubility and precipitation.
- Affected by temperature, pH, and ion concentration.
Quiz: Test Your Knowledge
- Define solubility product and explain its role in equilibrium.
- Write the Ksp expression for BaSO4.
- How does common ion effect alter solubility?
- Relate molar solubility and Ksp for AB2.
- List factors affecting solubility product.
Quiz Answers
- It is the equilibrium constant for dissolution of sparingly soluble salts.
- Ksp = [Ba2+] × [SO42-]
- It reduces solubility by shifting equilibrium to solid.
- Ksp = 4s3
- Temperature, pH, and common ions.
MCQs
- Ksp applies to:
- a) All ionic compounds
- b) Sparingly soluble salts ✔
- c) Gases
- d) Strong electrolytes
- For CaF2:
- a) [Ca2+][F–]
- b) [Ca2+][F–]2 ✔
- c) [Ca2+]2[F–]
- Common ion effect decreases solubility by:
- a) Adding a common ion salt ✔
- b) Increasing T
- c) Dilution
- Units of Ksp:
- a) mol/L
- b) Depends on salt’s formula ✔
- c) atm
MCQ Explanations
- Ksp is defined only for sparingly soluble salts.
- Stoichiometry of CaF2 gives [Ca2+] [F–]2.
- Common ion reduces ionization, lowering solubility.
- Units vary depending on exponents in expression.
NCERT Chemistry Textbook | Chem LibreTexts
