Stoichiometry in Mole Concept
What is Stoichiometry?
Stoichiometry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. It helps predict how much product will form from given reactants or how much reactant is needed for a desired product amount.
Importance of Stoichiometry
- Calculates amounts of substances consumed and produced.
- Essential for laboratory experiments and industrial chemical synthesis.
- Based on balanced chemical equations giving mole ratios.
Role of Mole Concept in Stoichiometry
The mole concept allows chemists to count particles and convert mass to moles. Using mole ratios from balanced equations, quantities of reactants and products can be accurately calculated.
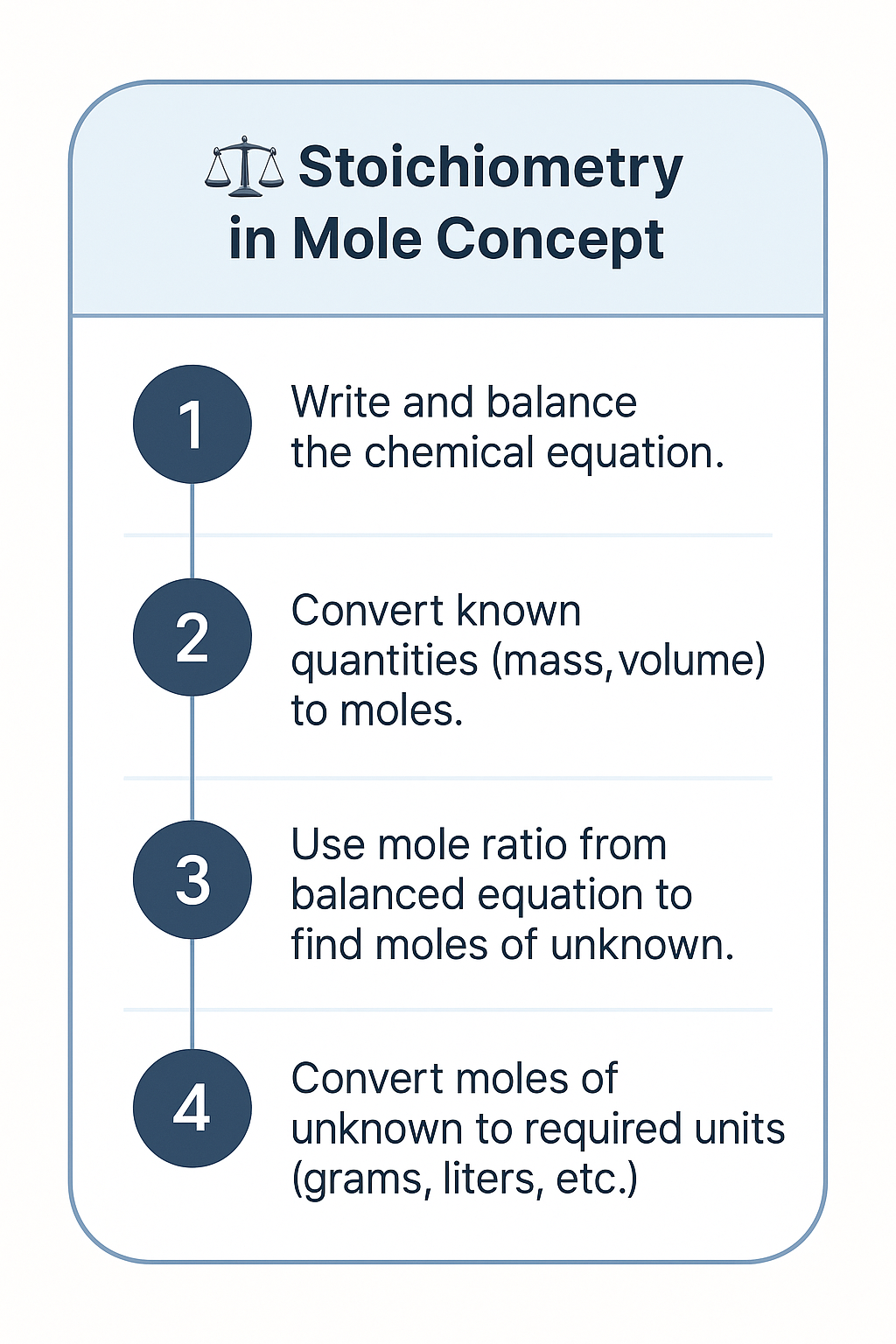
Key Steps in Stoichiometric Calculations
- Write and balance the chemical equation.
- Convert known quantities (mass, volume) to moles.
- Use mole ratio from balanced equation to find moles of unknown.
- Convert moles of unknown to required units (grams, liters, etc.).
Types of Stoichiometric Problems
- Mass to mass calculations.
- Mass to volume calculations.
- Volume to volume calculations (for gases under same conditions).
- Limiting reagent identification.
- Percent yield calculations.
Example Calculation
Given reaction: 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
How many grams of water are formed from 4 g of hydrogen?
1. Calculate moles of hydrogen:n = mass / molar mass = 4 / 2 = 2 moles
2. Use mole ratio (2 H2 : 2 H2O = 1:1):
Moles of water produced = 2 moles
3. Calculate mass of water:mass = moles × molar mass = 2 × 18 = 36 g
Stoichiometry combined with mole concept enables precise quantitative predictions in chemical reactions.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
- What is the molar mass of water?
A. 16 g/mol
B. 18 g/mol ✅
C. 20 g/mol
D. 22 g/mol - In the reaction 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O, how many moles of oxygen are required to produce 4 moles of water?
A. 2 moles ✅
B. 4 moles
C. 1 mole
D. 3 moles
True or False with Explanations
- Stoichiometry is only used for theoretical chemistry. – False
➤ Explanation: Stoichiometry is crucial in both theoretical and practical chemistry such as labs and industry. - The mole concept allows conversion between grams and moles. – True
➤ Explanation: This is fundamental to stoichiometric calculations.
Quick Quiz
Q: If 44 g of CO2 is produced, how many moles of CO2 are formed? (Molar mass = 44 g/mol)
Answer: 1 mole (since n = 44/44 = 1 mole)
Explore more:

Pingback: Mole Concept क्या है? Physical Chemistry का सबसे important topic है।