Hybridization
Hybridization is a concept in chemistry where atomic orbitals mix to form new equivalent orbitals called hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals explain molecular shapes and bonding properties more accurately than simple atomic orbitals.
What is Hybridization?
When atoms form covalent bonds, their atomic orbitals (s, p, d) combine or “hybridize” to create orbitals that are equal in energy (degenerate) and directed in specific geometries matching the observed molecular shapes.
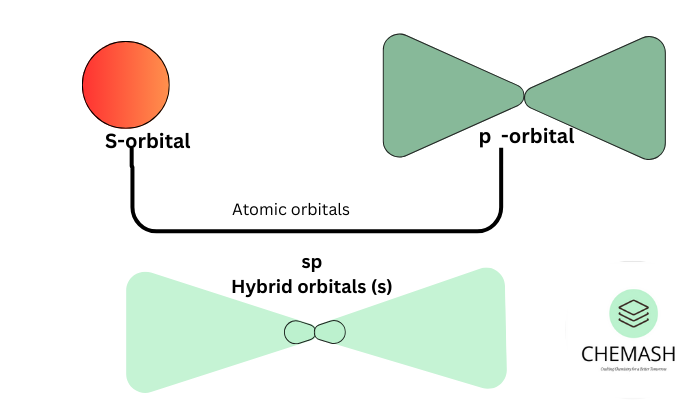
Types of Hybridization
- sp: Linear geometry, 180°. Example: BeCl2, C2H2.
- sp2: Trigonal planar, 120°. Example: BF3, C2H4.
- sp3: Tetrahedral, 109.5°. Example: CH4, NH3.
- sp3d: Trigonal bipyramidal, 90°/120°. Example: PCl5.
- sp3d2: Octahedral, 90°. Example: SF6.
Hybridization and Molecular Geometry
| Hybridization | Orbitals | Geometry | Bond Angle | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp | 2 | Linear | 180° | BeCl2, C2H2 |
| sp2 | 3 | Trigonal planar | 120° | BF3, C2H4 |
| sp3 | 4 | Tetrahedral | 109.5° | CH4, NH3, H2O |
| sp3d | 5 | Trigonal bipyramidal | 90°, 120° | PCl5 |
| sp3d2 | 6 | Octahedral | 90° | SF6 |
Limitations of Hybridization
- Qualitative model, no exact energy values.
- Cannot explain magnetic behavior.
- Fails for delocalized electrons (e.g., benzene).
- Not always applicable to transition metal complexes.
Quiz: Test Your Understanding
- What is hybridizations and why does it occur?
- What is the geometry and bond angle for sp3 hybridizations?
- Give an example of a molecule with sp2 hybridizations.
- How many hybrid orbitals are formed in sp3d hybridization?
- List one limitation of the hybridization concept.
Answers
- Hybridizations is orbital mixing to form equivalent orbitals, explaining molecular shapes and bonding.
- Tetrahedral geometry, ~109.5°.
- BF3 (boron trifluoride).
- Five hybrid orbitals.
- It is qualitative and cannot explain all properties.
MCQs
- Which molecule shows sp hybridizations?
a) CH4 b) BeCl2 c) NH3 d) H2O
✅ Correct: b) BeCl2 (linear, 180°) - Bond angle in sp2 hybridization?
a) 90° b) 120° c) 109.5° d) 180°
✅ Correct: b) 120° - Which has sp3d2 hybridization?
a) SF6 b) BF3 c) NH3 d) C2H2
✅ Correct: a) SF6 (octahedral, 90°)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is hybridizations?
A: Mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals, explaining bonding and geometry.
Q2: What is the bond angle in sp3?
A: Approximately 109.5°.
Q3: Which molecule has trigonal planar geometry?
A: BF3.
Learn more: Orbital Hybridization (Wikipedia) |
