Polymers are large molecules composed of repeating structural units (monomers). They are essential in modern life with applications in packaging, textiles, healthcare, aerospace, and more. This article explains the most important polymers, their properties, and applications.
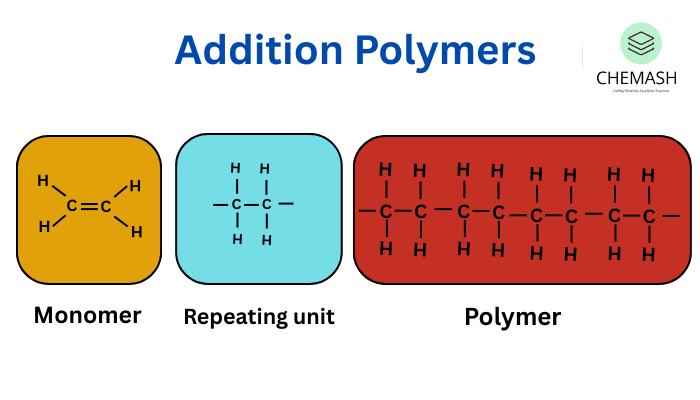
1. Polyethylene (PE)
- Type: Addition polymer
- Monomer: Ethylene (CH₂=CH₂)
- Properties: Lightweight, chemically resistant, good insulator
- Applications: Plastic bags, bottles, containers, wire insulation
2. Polypropylene (PP)
- Type: Addition polymer
- Monomer: Propylene (CH₂=CHCH₃)
- Properties: Flexible, fatigue resistant, high melting point
- Applications: Food containers, textiles, automotive parts
3. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
- Type: Addition polymer
- Monomer: Vinyl chloride (CH₂=CHCl)
- Properties: Rigid or flexible, weather resistant, flame retardant
- Applications: Pipes, window frames, flooring, credit cards
4. Polystyrene (PS)
- Type: Addition polymer
- Monomer: Styrene (C₆H₅CH=CH₂)
- Properties: Transparent, brittle, easy to mold
- Applications: Disposable cutlery, insulation foam, CD cases
5. Teflon (PTFE – Polytetrafluoroethylene)
- Type: Addition polymer
- Monomer: Tetrafluoroethylene (CF₂=CF₂)
- Properties: Non-reactive, high heat resistance, low friction
- Applications: Non-stick cookware, gaskets, lubricants
6. Nylon-6,6
- Type: Condensation polymer
- Monomers: Hexamethylenediamine + Adipic acid
- Properties: Strong, abrasion resistant, high tensile strength
- Applications: Fabrics, parachutes, ropes, tire cords
7. Bakelite
- Type: Thermosetting polymer
- Monomers: Phenol + Formaldehyde
- Properties: Hard, brittle, heat resistant, non-conductive
- Applications: Electrical switches, handles, casings
8. Polyesters (e.g., PET, Terylene)
- Type: Condensation polymer
- Monomers: Terephthalic acid + Ethylene glycol
- Properties: Wrinkle-resistant, strong, moisture-resistant
- Applications: Clothing, packaging bottles, magnetic tapes
9. Polyacrylonitrile (PAN)
- Type: Addition polymer
- Monomer: Acrylonitrile (CH₂=CHCN)
- Properties: High strength, chemical resistance
- Applications: Synthetic wool (Orlon), fibers, carbon fiber precursor
10. Biopolymers
- Examples: Cellulose, Starch, Proteins, DNA
- Source: Plants, animals, microbes
- Applications: Biodegradable packaging, drug delivery, food industry
Quiz: Important Polymers
Q1. Which polymer is widely used to make non-stick cookware?
✔ Answer: Teflon – due to its non-reactive, slippery surface.
Q2. Which polymer is made from phenol and formaldehyde?
✔ Answer: Bakelite – a thermosetting polymer.
Q3. What is the monomer of polystyrene?
✔ Answer: Styrene
Q4. Nylon-6,6 is formed from which monomers?
✔ Answer: Hexamethylenediamine and Adipic acid
Related reading: Polymerization Reactions | Polymer Chemistry (ScienceDirect)
