Integrated Rate Laws: Understanding Reactions Over Time
Integrated rate laws explain how the concentration of reactants changes with time during a chemical reaction. They are a core part of Chemical Kinetics and are widely used to predict reaction duration and behavior.
This topic is extremely important for Class 11, Class 12, NEET, JEE and other competitive exams.
Table of Contents
- Why Integrated Rate Laws Are Important
- Types of Integrated Rate Laws
- Zero-Order Reaction
- First-Order Reaction
- Second-Order Reaction
- Summary Table
- MCQs
- FAQs
Why Are Integrated Rate Law Important?
- Predict how long a reaction will take
- Calculate remaining reactant at any time
- Determine the order of reaction
- Calculate half-life of reactions
Types of Integrated Rate Law
Integrated rate laws are classified based on the order of reaction.
Zero-Order Reaction
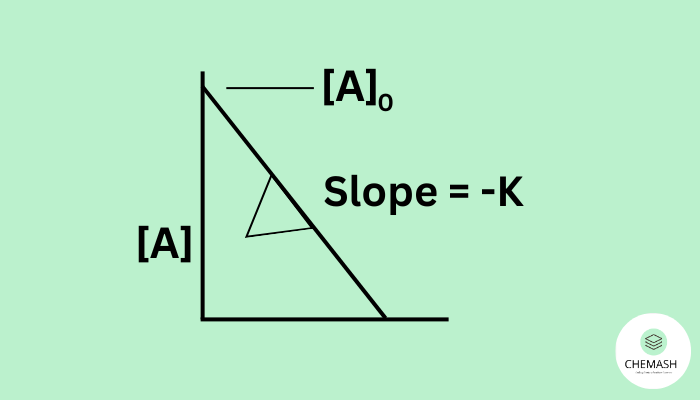
In a zero-order reaction, the rate of reaction is independent of reactant concentration.
Integrated Rate Law:
[A] = [A]0 − kt
Graph: [A] vs. time → straight line (slope = −k)
Half-life:
t1/2 = [A]0 / 2k
Example: Drug degradation at constant rate
First-Order Reaction
In a first-order reaction, the rate is directly proportional to the concentration of one reactant.
Integrated Rate Law:
[A] = [A]0e−kt
or
ln[A] = ln[A]0 − kt
Graph: ln[A] vs. time → straight line
Half-life:
t1/2 = 0.693 / k (independent of concentration)
Examples: Radioactive decay, drug metabolism
Second-Order Reaction
In a second-order reaction, the rate depends on the square of reactant concentration or two reactants.
Integrated Rate Law:
1/[A] = 1/[A]0 + kt
Graph: 1/[A] vs. time → straight line
Half-life:
t1/2 = 1 / (k[A]0)
Examples: Dimerization reactions
Summary Table of Integrated Rate Laws
| Order | Linear Graph | Half-Life | Depends on [A]0? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zero | [A] vs. t | [A]0 / 2k | Yes |
| First | ln[A] vs. t | 0.693 / k | No |
| Second | 1/[A] vs. t | 1 / (k[A]0) | Yes |
Exam-Oriented MCQs
Q1. Which plot is linear for a first-order reaction?
A) [A] vs. t B) ln[A] vs. t C) 1/[A] vs. t D) Rate vs. t
Q2. Half-life of a first-order reaction depends on:
A) Initial concentration B) Rate constant C) Time D) Pressure
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. Why are integrated rate law important?
Answer: They help predict reaction time, concentration changes, and reaction order.
Q. Which integrated rate law has constant half-life?
Answer: First-order reaction.
© 2025 CHEMASH | Physical Chemistry
