Updated on September 2025
What is Organic Chemistry?
Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that studies compounds containing carbon. Due to its ability to form strong covalent bonds with itself and other atoms like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens, carbon can create a vast number of compounds.
Why is it Called “Organic” Chemistry?
Historically, it was believed that organic compounds could only be produced by living organisms. This theory was overturned in 1828 when Friedrich Wöhler synthesized urea (NH₂CONH₂) from an inorganic salt, ammonium cyanate.
NH₄OCN → NH₂CONH₂ (Ammonium cyanate → Urea)
Unique Characteristics of Organic Compounds
- Catenation: Ability of carbon to form chains and rings.
- Tetravalency: Carbon forms 4 stable covalent bonds.
- Isomerism: Compounds with the same formula but different structures.
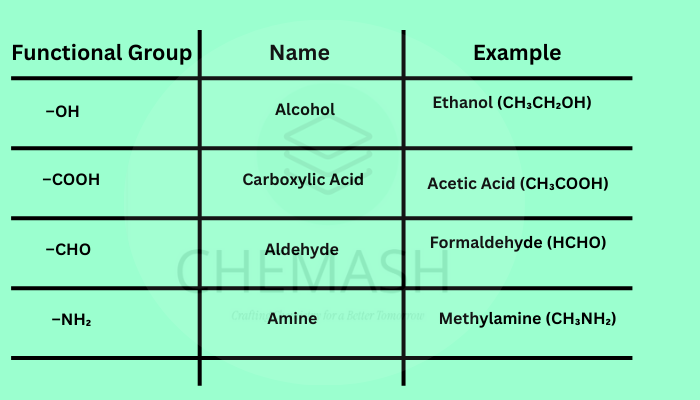
- Functional Groups: Specific groups like –OH, –COOH, –NH₂ determine reactivity.
Classification of Organic Compounds
- Acyclic: Open-chain compounds (e.g., Butane C₄H₁₀).
- Cyclic: Ring compounds
- Aliphatic (non-aromatic) – Cyclohexane
- Aromatic – Benzene (C₆H₆)
- Heterocyclic: Rings with non-carbon atoms (e.g., Pyridine).
Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry
Importance of Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry plays a vital role in:
- Pharmaceuticals: Medicines like aspirin, penicillin.
- Agriculture: Fertilizers, pesticides.
- Polymers: Plastics like PVC, nylon.
- Biochemistry: Proteins, DNA, carbohydrates.
- Energy: Fuels like methane, gasoline.
Organic Chemistry Quiz – Test Yourself!
Here’s a quick quiz with answers and explanations:
- Which element is the backbone of all organic compounds?
Answer: Carbon ✅ - Who synthesized urea artificially?
Answer: Friedrich Wöhler ✅ - Which functional group defines alcohols?
Answer: –OH ✅ - Example of a saturated hydrocarbon?
Answer: Ethane ✅ - Which is an aromatic compound?
Answer: Benzene ✅
Full quiz with 10 questions available at the bottom of this article.
FAQs – Organic Chemistry Basics
1. Why is carbon important in chemistry?
Because of its unique bonding properties, it can form millions of compounds.
2. What is the difference between aliphatic and aromatic compounds?
Aliphatic compounds don’t have delocalized electrons, while aromatics (like benzene) do.
3. What are examples of natural vs synthetic organic compounds?
Natural: Glucose, proteins. Synthetic: Nylon, PVC, polyethylene.
हिंदी अनुवाद (Bilingual Support)
कार्बनिक रसायन विज्ञान कार्बन युक्त यौगिकों का अध्ययन है। यह चिकित्सा, कृषि, ऊर्जा और जीवन विज्ञान में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है। कार्बन की चतुष्वैलेंसी (चार सहसंयोजक बंध बनाना) और श्रृंखला बनाने की क्षमता (कैटेनेशन) इसे अद्वितीय बनाती है।

Pingback: Derivatives in Organic Chemistry | Types, Formation, and Uses - CHEMASH