Ionic Equilibrium
Balance between ionization and recombination in aqueous solutions
What is Ionic Equilibrium?
Ionic equilibrium is the state in an electrolyte solution where the rate of ionization equals the rate of recombination. It ensures a constant concentration of ions over time. This equilibrium is central to acid-base reactions, buffer systems, and many biological processes.
Types of Electrolytes
- Strong Electrolytes: Fully dissociate in water (e.g., HCl, NaCl).
- Weak Electrolytes: Partially dissociate, forming an equilibrium (e.g., CH₃COOH).
Ionization Constant (Ka)
The ionization constant Ka measures the strength of weak acids:
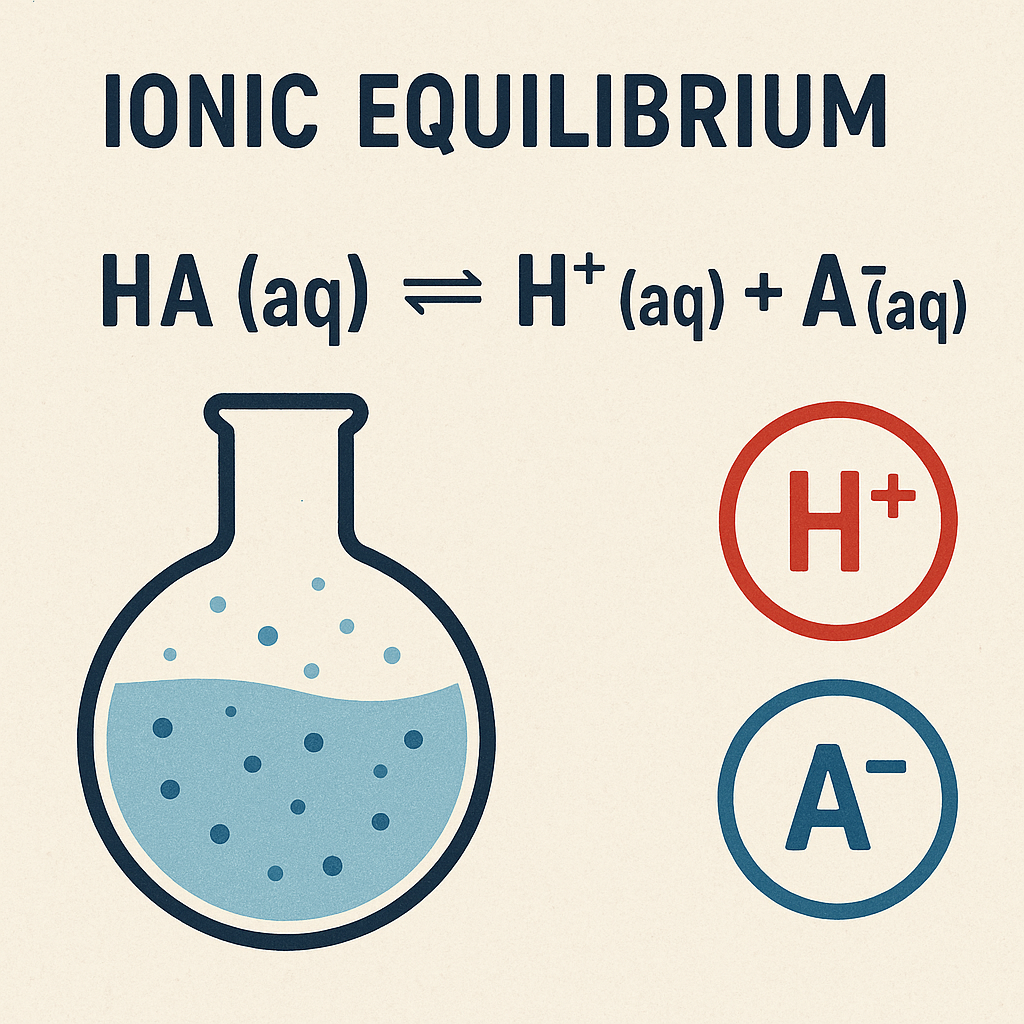
HA ⇌ H+ + A–
Ka = [H+][A–] / [HA]
Water Ionization and Kw
Even pure water ionizes:
2H₂O ⇌ H₃O+ + OH–
Kw = [H+][OH–] = 1.0 × 10⁻¹⁴ at 25°C
Common Ion Effect
Adding a common ion (already present in solution) reduces ionization of weak electrolytes. E.g., Adding NaCH₃COO reduces CH₃COOH ionization.
Salt Hydrolysis
When salts like NH₄Cl or CH₃COONa dissolve, their ions may react with water, shifting pH. This is called hydrolysis.
Internal Links
- https://chemash.in/buffer-solutions-chemical-equilibrium/
- https://chemash.in/acid-rain/
- https://chemash.in/hydrolysis-of-salts/
External References
MCQs – Ionic Equilibrium
- Which of the following is a strong electrolyte?
a) CH₃COOH
b) NH₃
c) NaCl ✅
d) HCN
Explanation: NaCl fully dissociates in water, making it a strong electrolyte. - What is the value of Kw at 25°C?
a) 1.0 × 10⁻⁷
b) 1.0 × 10⁻¹⁴ ✅
c) 1.0 × 10⁻³
d) 1.0 × 10⁻¹⁰
Explanation: Kw = [H+][OH–] = 10⁻⁷ × 10⁻⁷ = 10⁻¹⁴ at 25°C.
True/False Questions
- True: Acetic acid is a weak electrolyte. ✅
- False: All salts are neutral in solution. ❌ (Some cause acidic or basic hydrolysis)
- True: Common ion effect suppresses ionization. ✅
Quick Quiz
Which of the following will increase the ionization of a weak acid?
- a) Adding more of its conjugate base
- b) Increasing H⁺ concentration
- c) Removing H⁺ ions ✅
- d) Adding NaCl
Explanation: Removing H⁺ shifts equilibrium to the right (Le Chatelier’s Principle).
Conclusion: Mastering ionic equilibrium is essential for competitive exams and real-world chemistry applications like drug formulation, pH balancing, and biochemical reactions.
pH scale with acid-base titration and ions in solution.
