Introduction to Ketones
Ketones are a class of organic compounds containing a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to two carbon atoms. Their general formula is R–CO–R', where R and R′ can be the same or different alkyl or aryl groups.
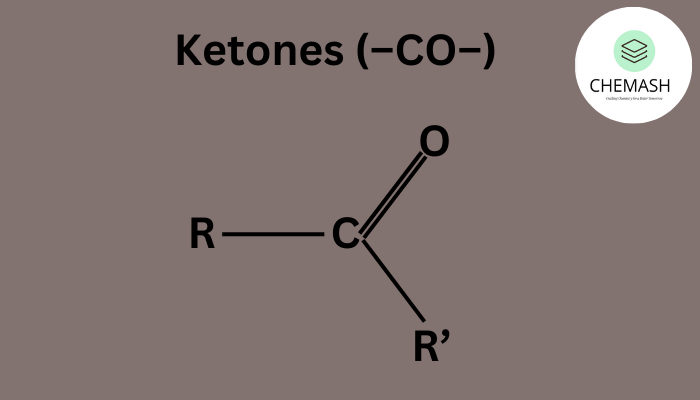
Key Characteristics
- Functional group: Carbonyl group (C=O) within the carbon chain.
- Position: Carbonyl carbon is bonded to two other carbon atoms (unlike aldehydes).
- Polarity: Ketones are polar due to the electronegative oxygen atom.
- Hydrogen bonding: Cannot form hydrogen bonds with themselves (only with water).
Structure of Ketones
The carbonyl carbon in ketones is sp² hybridized, making the structure planar around the carbonyl group. The angle between substituents is approximately 120°.
The carbon–oxygen double bond consists of a sigma (σ) bond and a pi (π) bond. The oxygen has a partial negative charge, making the carbon electrophilic.
Nomenclature of Ketones
- IUPAC Name: Based on the longest carbon chain containing the ketone group. Replace
-eof alkane with-one. - Examples:
- CH₃–CO–CH₃ → Propan-2-one (Common name: Acetone)
- CH₃–CO–C₂H₅ → Butan-2-one
Physical Properties of Ketones
- Moderate boiling points (higher than alkanes, lower than alcohols).
- Soluble in water (small ketones) due to hydrogen bonding with water molecules.
- Colorless liquids with a sweet or pungent odor.
Common Examples of Ketones
- Acetone: CH₃COCH₃ – used in nail polish remover.
- Butanone: CH₃COC₂H₅ – used as a solvent.
- Camphor: Natural ketone used in balms and vaporizers.
Quick MCQ Quiz on Ketones
- What is the functional group of ketones?
a) –OH
b) –CHO
c) –CO–
d) –COOH
Answer: c) –CO– - Which of the following is the simplest ketone?
a) Methanol
b) Acetone
c) Ethanal
d) Butanone
Answer: b) Acetone - What is the hybridization of the carbonyl carbon in ketones?
a) sp
b) sp²
c) sp³
d) dsp²
Answer: b) sp² - Which ketone is naturally found in camphor?
a) Acetone
b) Butanone
c) Camphor
d) Propanone
Answer: c) Camphor - Ketones cannot form hydrogen bonds with:
a) Water molecules
b) Alcohols
c) Themselves
d) Amines
Answer: c) Themselves
True or False
- Ketones have the general formula R–CO–R′. True ✅
- Ketones can hydrogen bond with themselves. False ❌ (They can only bond with water molecules)
- The carbonyl carbon in ketones is sp² hybridized. True ✅
- All ketones are insoluble in water. False ❌ (Small ketones are soluble)
Related Topics: Aldehydes, Alcohols
External Resource: Wikipedia – Ketones, NCERT Chemistry Class 12.

Pingback: nomenclature-of-aldehydes-and-ketones