Metabolism – Definition, Types, Functions, Pathways & Regulation
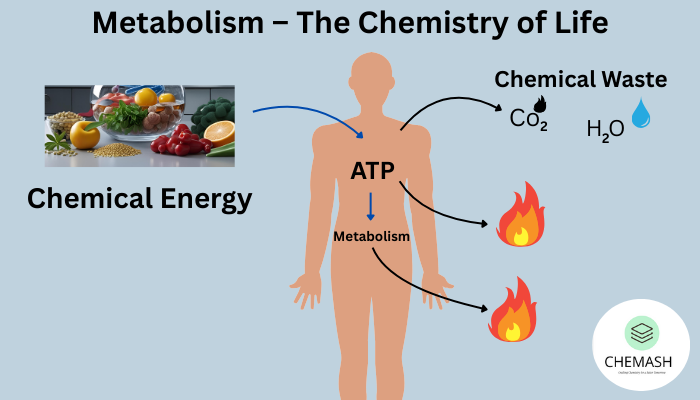
Metabolism refers to the complete set of biochemical reactions occurring within living cells. These metabolic reactions are essential for growth, energy production, maintenance, and survival of organisms.
According to Encyclopaedia Britannica , metabolisms includes all chemical transformations that occur in living organisms.
Table of Contents
- What is Metabolisms?
- Types of Metabolism: Catabolism & Anabolism
- Functions of Metabolism
- Key Metabolic Pathways
- Role of Enzymes in Metabolism
- Regulation of Metabolism
- Biological Importance
- FAQs
- MCQs & Practice Questions
What is Metabolism in Biology?
Metabolisms is defined as the sum total of all biochemical reactions that occur inside a living organism to sustain life.
Metabolism = Catabolism + Anabolism
Types of Metabolisms: Catabolism and Anabolism
Catabolic Metabolism (Energy-Releasing Reactions)
Catabolism involves the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones with the release of energy.
- Glycolysis
- Cellular respiration
Anabolic Metabolisms (Biosynthetic Reactions)
Anabolism involves the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler precursors using energy.
- Protein synthesis
- DNA replication
Main Functions
- Energy production and storage (ATP formation)
- Building cellular and tissue structures
- Synthesis of biomolecules like proteins and lipids
- Removal of metabolic waste
- Regulation of cellular responses
Key Metabolic Pathways in Living Organisms
Glycolysis Pathway
Breakdown of glucose into pyruvate with ATP production.
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
Aerobic pathway generating NADH and FADH₂.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
Produces large amounts of ATP in mitochondria.
Photosynthesis as a Metabolic Pathway
Conversion of solar energy into chemical energy.
Gluconeogenesis
Formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources.
Role of Enzymes
All metabolic reactions are catalyzed by enzymes, which lower activation energy and increase reaction efficiency.
Example: Amylase catalyzes starch breakdown.
Regulation
- Feedback inhibition
- Hormonal regulation (insulin, glucagon)
- Temperature and pH control
- Availability of substrates
Biological Importance
- Sustains life processes
- Maintains energy balance
- Helps diagnose metabolic disorders
- Essential for homeostasis
FAQs
What is metabolisms?
Metabolisms is the total of all chemical reactions in a living organism.
What are the two types of metabolisms?
Catabolism and Anabolism.
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1. Which of the following is an anabolic process?
a) Glycolysis b) Protein synthesis ✅ c) Krebs cycle d) Fermentation
Q2. The powerhouse of the cell is:
Answer: Mitochondria
