Neutralization Reactions
A neutralization reaction is a chemical process in which an acid and a base react to form a salt and water. Hydrogen ions (H+) from the acid combine with hydroxide ions (OH−) from the base to yield H2O. Neutralization Reactions
These reactions are important in laboratory analysis, industry, agriculture and everyday life — for pH regulation, treating acidic or basic wastes, and in products like antacids and soaps.
General Equation
Acid + Base → Salt + Water
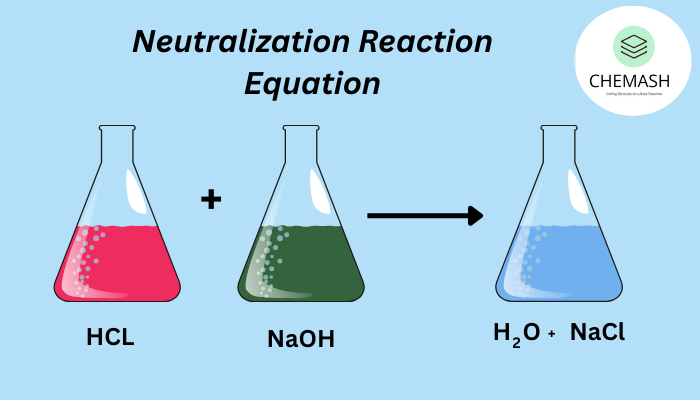
Example: HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
Types of Neutralization Reactions
- Strong acid + strong base: HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O (complete neutralization)
- Strong acid + weak base: HCl + NH4OH → NH4Cl + H2O
- Weak acid + strong base: CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O
- Weak acid + weak base: CH3COOH + NH4OH → NH4CH3COO + H2O
Ionic Perspective
The net ionic equation for most neutralizations:
H+(aq) + OH−(aq) → H2O(l)
Real-life Applications
- Antacids: Neutralize excess stomach acid (eg. milk of magnesia — Mg(OH)2).
- Soil treatment: Lime (Ca(OH)2) is added to acidic soils to raise pH.
- Waste treatment: Neutralizing acidic or basic industrial effluents before disposal.
- Personal care: Adjusting pH in cosmetics and soaps to be skin-friendly.
Important Considerations
- The salt formed may be neutral, acidic or basic depending on acid/base strength.
- Neutralizations are typically exothermic (release heat).
- Used in titration to determine unknown concentrations.
Summary Table
| Reactants | Salt Formed | Type |
|---|---|---|
| HCl + NaOH | NaCl | Strong acid + strong base |
| H2SO4 + NH4OH | (NH4)2SO4 | Strong acid + weak base |
| CH3COOH + NaOH | CH3COONa | Weak acid + strong base |
Related: Types of Salts
Further reading: Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Quiz: Neutralization Reactions
Q1: What is always formed in a neutralization reaction?A) Only saltB) Only waterC) Salt and waterD) Acid and base
Answer: C) Salt and water — Neutralization yields salt and water as products.
Q2: Which of these is a neutralization reaction?A) NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H₂OB) Zn + HCl → ZnCl₂ + H₂C) AgNO₃ + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO₃D) Na₂CO₃ + HCl → CO₂ + H₂O + NaCl
Answer: A) NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H₂O — direct acid-base neutralization forming salt and water.
Q3: Which salt is produced when H₂SO₄ reacts with NaOH?A) NaClB) Na₂SO₄C) NaHSO₄D) Na₂CO₃
Answer: B) Na₂SO₄ — Two moles of NaOH neutralize one mole of H₂SO₄ to form sodium sulfate.
Select an option to reveal whether it’s correct. Explanations appear after selection.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can neutralization produce a basic or acidic salt?
A: Yes. If a weak acid reacts with a strong base, the resulting salt may be basic in solution; conversely, a strong acid + weak base can give an acidic salt.
Q: Are all neutralization reactions exothermic?
A: Most neutralizations release heat (exothermic), but the amount varies with reactants and concentrations.
Published by CHEMASH • September 13, 2025
Slug: neutralization-reactions • Tags: neutralization, acid-base, chemistry, MCQ, quiz
