Table of Contents
- General Formula & Structure
- Nomenclature
- Sources of Carboxylic Acids
- Physical Properties
- Chemical Characteristics
- FAQs
- Quiz
Carboxylic acids are an important class of organic compounds, identified by the presence of a carboxyl group (–COOH). This consists of a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a hydroxyl group (–OH), making them acidic in nature.
General Formula and Structure
The general formula is R–COOH, where R = alkyl/aryl group.
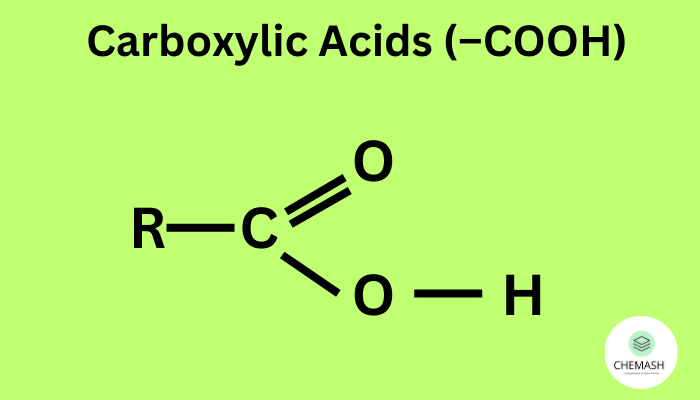
The carboxyl group is planar and stabilized by resonance between carbonyl and hydroxyl groups.
Nomenclature
- IUPAC: Replace alkane
-ewith-oic acid. Example: methane → methanoic acid. - Common: Historical names such as formic acid (HCOOH), acetic acid (CH3COOH).
| Formula | Common Name | IUPAC Name |
|---|---|---|
| HCOOH | Formic acid | Methanoic acid |
| CH3COOH | Acetic acid | Ethanoic acid |
| CH3CH2COOH | Propionic acid | Propanoic acid |
Sources of Carboxylic Acids
- Formic acid → ant/bee stings
- Acetic acid → vinegar
- Citric acid → citrus fruits
- Fatty acids (oleic acid) → oils & fats
Physical Properties
- Low carboxylic acids = liquids with pungent odor.
- Polar, hydrogen bonding → high boiling points.
- Highly soluble (small acids), solubility decreases with chain length.
Chemical Characteristics
Carboxylic acids are weak acids but stronger than alcohols/phenols. Reactions include:
- Formation of salts with bases
- Esterification with alcohols
- Reduction to alcohols
- Decarboxylation
FAQs
Q1: Why are carboxylic acids acidic?
Because the –COOH group can donate a proton (H⁺) and the conjugate base is resonance-stabilized.
Q2: Which is stronger – acetic acid or ethanol?
Acetic acid, because its conjugate base (acetate ion) is stabilized by resonance.
Q3: What is the pKa range of carboxylic acids?
Typically between 4 and 5, making them weak acids but stronger than alcohols and phenols.
Quick Quiz
MCQ
1. Which of the following is the IUPAC name of acetic acid?
- A) Methanoic acid
- B) Propanoic acid
- C) Ethanoic acid ✅
- D) Butanoic acid
Fill in the Blanks
2. The general formula of carboxylic acids is ______.
Answer: R–COOH
3. Formic acid is found in ______ stings.
Answer: Ant and bee
Conclusion: Carboxylic acids are biologically and industrially vital compounds, showing versatile reactivity due to their –COOH group.

Perfect piece of work you have done, this site is really cool with great info .