Ozone Depletion & Acid Rain
Explore the chemistry, causes, and effects of Ozone Depletion and Acid Rain — two major environmental challenges affecting our planet.
The ozone layer is a region in the Earth’s stratosphere that absorbs most of the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV-B and UV-C) radiation, located about 15–35 km above Earth.
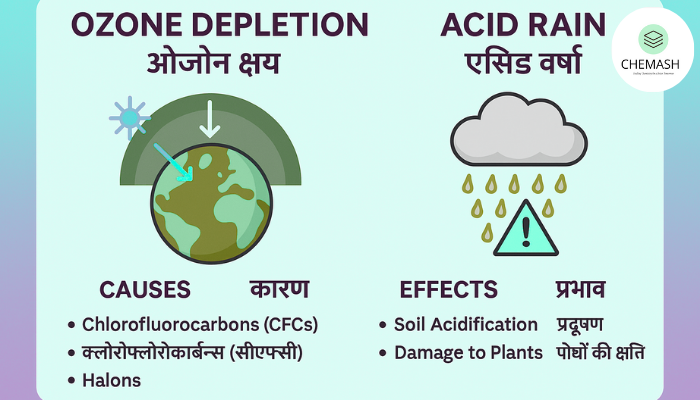
Ozone depletion refers to the thinning of this layer, mainly caused by human-made chemicals such as CFCs and halons. These compounds release chlorine and bromine atoms that catalytically destroy ozone molecules. Ozone Layer and Its Depletion
A detailed look into two major atmospheric environmental issues threatening ecosystems and human health.
Chemistry Behind Ozone Depletion
The process involves the following chain reaction:
- CFCl₃ → CFCl₂ + Cl• (under UV light)
- Cl• + O₃ → ClO• + O₂
- ClO• + O → Cl• + O₂
One chlorine atom can destroy more than 100,000 ozone molecules before being deactivated.
Learn more: Environmental Chemistry – CHEMASH
Environmental and Health Impacts
- Increased UV exposure leads to skin cancer and cataracts.
- Damage to phytoplankton affects aquatic ecosystems.
- Reduced crop yield due to DNA damage in plants.
- Weakening of building materials and plastics.
Acid Rain: Causes and Effects
Acid rain is rainwater with pH lower than 5.6, caused by the dissolution of acidic oxides like SO₂ and NOₓ in water vapor to form acids:
- SO₂ + H₂O → H₂SO₃ → H₂SO₄ (after oxidation)
- 2NO₂ + H₂O → HNO₂ + HNO₃
Main sources: Fossil fuel combustion in industries and vehicles.
Impacts of Acid Rain
- Soil acidification lowers fertility and leaches nutrients.
- Acidification of lakes kills aquatic species.
- Corrosion of monuments (e.g., Taj Mahal).
- Forest decline due to leaf and root damage.
Quiz – Ozone Depletion & Acid Rain
- Which compound is mainly responsible for ozone depletion?
✅ Answer: CFCs — Chlorofluorocarbons release chlorine atoms under UV light that destroy ozone molecules. - Which layer of the atmosphere contains the ozone layer?
✅ Answer: Stratosphere — It lies between 15–35 km above Earth. - Which gas is NOT a contributor to acid rain?
✅ Answer: NH₃ — Ammonia is alkaline and neutralizes acids. - Which monument is most affected by acid rain?
✅ Answer: Taj Mahal — Acid rain erodes its marble (CaCO₃).
FAQs – Ozone Depletion & Acid Rain
Q1. What is the ozone hole?
The ozone hole is a seasonal thinning of the ozone layer over Antarctica caused by CFCs and cold stratospheric conditions.
Q2. How can we reduce acid rain?
By reducing fossil fuel use, installing scrubbers in power plants, and shifting to renewable energy sources.
Q3. Is acid rain harmful to humans?
Indirectly yes — it contaminates water, damages crops, and increases respiratory issues. Up Next: Air Quality Index & Pollution Control Measures 🌫️
© 2025 CHEMASH — Educational Chemistry Resources
