Phenol (C₆H₅OH)
Phenol is an aromatic compound consisting of a hydroxyl group (–OH) bonded directly to a benzene ring. It is the simplest member of the phenol family and plays a crucial role in organic chemistry and industry.
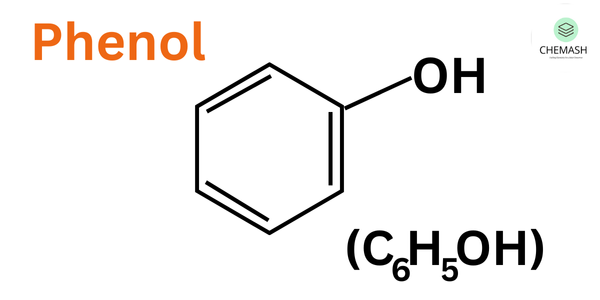
Structure:
C₆H₅–OH
It has a planar benzene ring with sp² hybridized carbon atoms and a hydroxyl group attached to one carbon, allowing resonance interaction between the ring and the lone pair on oxygen.
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Colorless crystalline solid (turns pink/brown on exposure to air)
- Melting Point: 40.5°C
- Boiling Point: 181.7°C
- Slightly soluble in water; highly soluble in alcohol, ether
- Has a distinct medicinal odor
Preparation Methods:
- From Benzene Sulphonic Acid: C₆H₅SO₃H + NaOH → C₆H₅OH
- From Diazonium Salt: C₆H₅–N₂⁺Cl⁻ + H₂O → C₆H₅OH + N₂ + HCl
- From Cumene (Industrial): Cumene → Cumene hydroperoxide → Phenol + Acetone
Chemical Properties:
1. Acidic Nature
Phenol is more acidic than alcohols due to resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion.
2. Electrophilic Substitution Reactions
- Nitration → o- & p-nitrophenol
- Halogenation → 2,4,6-tribromophenol
- Friedel-Crafts → aryl ketones
3. Esterification
Phenol reacts with acyl/benzoyl chloride to form esters.
4. Reaction with Zinc
C₆H₅OH + Zn → C₆H₆ + ZnO
Important Reactions:
| Reaction | Equation |
|---|---|
| Nitration | C₆H₅OH + HNO₃ → o-/p-Nitrophenol |
| Halogenation | C₆H₅OH + 3Br₂ → 2,4,6-Tribromophenol |
| With NaOH | C₆H₅OH + NaOH → C₆H₅ONa + H₂O |
Uses of Phenol:
- Disinfectants and antiseptics (Dettol)
- Manufacture of plastics (Bakelite)
- Synthesis of aspirin, dyes, explosives
- Pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries
Fun Fact:
Phenol was first extracted from coal tar and used by Joseph Lister as a surgical antiseptic!
🔗 Related Topics: Phenol (Wikipedia)
Practice Quiz on Phenol
MCQs:
- Phenol is more acidic than alcohol because:
- a) Higher molecular weight
- b) Resonance stabilization of phenoxide ion ✅
- c) Stronger O–H bond
- d) None of these
- Industrial preparation of phenol is commonly from:
- a) Cumene ✅
- b) Benzaldehyde
- c) Glucose
- d) Styrene
True/False:
- Phenol is less acidic than alcohol. ❌ (False)
- Phenol reacts with Br₂ water to give a white precipitate. ✅ (True)

Pingback: introduction-to-aldehydes-and-ketones