Position and Displacement — Class 9/10 Physics
Position and Displacement are two important concepts in Physics that describe the motion of an object. Understanding the difference between them helps in solving numerical problems in kinematics.
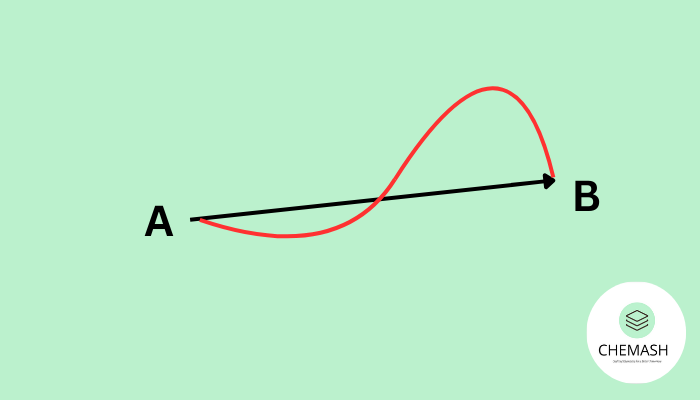
What is Position?
Position is the location of an object relative to a reference point (called the origin). It tells us where an object is present at a given moment.
Key points:
- Position is written as x.
- It is measured from a reference point (origin).
- It has both magnitude and direction.
- Therefore, position is a vector quantity.
Example:
If a car is 30 m east of the origin, its position can be written as: x = + 30 m
What is Displacement?
Displacement (Δx) is the change in position of an object from its initial point to its final point. It does not consider the actual path taken — only the shortest distance between initial and final position.
Formula:
Δx = x₂ − x₁
- x₁ = Initial position
- x₂ = Final position
Important properties:
- Displacement can be positive, negative, or zero.
- It depends only on initial and final positions.
- It is a vector quantity.
Example:
A boy moves from 0 m to 50 m, then back to 30 m.
Displacement = 30 m (not 80 m)
Distance vs Displacement (Difference Table)
| Feature | Distance | Displacement |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Total path covered by object | Shortest distance between start & end points |
| Quantity type | Scalar | Vector |
| Path dependence | Path-dependent | Path-independent |
| Value | Always positive | Can be +, – or zero |
| Formula | No fixed formula | Δx = x₂ − x₁ |
Key Relation:
Distance ≥ |Displacement|
Numerical Example
A person walks from his house to the market (600 m), and then to a park (300 m). Final location is 300 m ahead of the house.
- Distance = 600 + 300 = 900 m
- Displacement = 300 m (from house to park)
MCQs — Practice Questions
- Which of the following is a vector quantity?
(a) Distance (b) Speed (c) Position (d) Time
Answer: (c) - If an object returns to its starting point, its displacement is:
(a) Positive (b) Negative (c) Zero (d) Maximum
Answer: (c) - Distance is always:
(a) Positive (b) Zero (c) Negative (d) Positive or Negative
Answer: (a)
Quick Quiz (Self-evaluation)
Try to answer without looking!
- A car moves from 20 m to 70 m. What is its displacement?
- Can displacement ever be greater than distance?
- If a person walks 5 km in a circle and returns to the same point, what is displacement?
Conclusion
Position tells us the exact location of an object, while displacement tells us how far and in which direction the object has moved from its initial position. Displacement focuses only on the shortest distance and is a vector quantity, whereas distance depends on the actual path taken and is a scalar quantity.
