Properties of Gases
Fundamental properties of gases include compressibility, expansion, low density, diffusion & effusion, pressure, and temperature dependence. Understanding these is essential in physics and chemistry applications.
Contents
- Compressibility
- Expansion
- Low Density (ρ = PM/RT)
- Diffusion & Effusion (Graham’s Law)
- Pressure
- Temperature Dependence
- Summary Table
- Concept Check — Quiz
- FAQ
- References & External Links
1. Compressibility
Gases are highly compressible because their particles are widely spaced. Applying pressure reduces volume significantly. This principle is used in pneumatic systems and gas cylinders.
2. Expansion
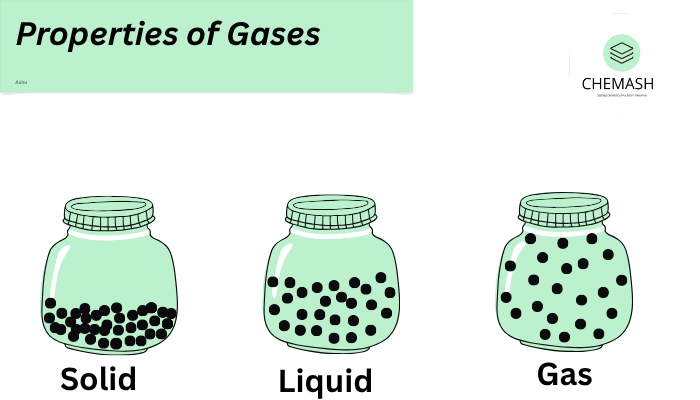
Gases expand to fill the entire volume of their container due to the random motion of particles. Unlike solids and liquids, gases do not have a fixed shape or volume.
3. Low Density
Gas density is much lower than that of liquids or solids. It can be calculated using the ideal gas formula:
ρ = PM / RT
- P = Pressure
- M = Molar mass of the gas
- R = Universal gas constant
- T = Absolute temperature (Kelvin)
4. Diffusion & Effusion
Diffusion is the spontaneous mixing of gas molecules. Effusion is the escape of gas through a small hole without collisions. Graham’s law governs the rates:
Rate ∝ 1 / √M
Lighter gases diffuse and effuse faster than heavier gases.
5. Pressure
Gas pressure arises from particles colliding with container walls. Defined as force per unit area:
- 1 atm = 101,325 Pa = 760 mmHg
6. Temperature Dependence
Temperature affects the average kinetic energy of gas molecules. Increasing temperature increases:
- Pressure at constant volume
- Volume at constant pressure
Summary Table: Properties of Gases
| Property | Description | Real-World Example |
|---|---|---|
| Compressibility | Ability to reduce volume under pressure | Oxygen tanks for diving |
| Diffusion | Spontaneous mixing of gas particles | Perfume smell spreading in a room |
| Low Density | Mass per unit volume is very small | Helium balloons floating |
Concept Check — Quiz
Q1: Which gas property explains why a balloon bursts when overfilled?
- a) Diffusion
- b) Expansion ✅
- c) Compressibility
- d) Density
Explanation: Gases expand to fill their container; overexpansion can cause rupture.
Q2: Which property allows gases to be stored in cylinders under high pressure?
- a) Low density
- b) Compressibility ✅
- c) Diffusion
- d) Effusion
Explanation: Gases compress significantly, allowing storage in small volumes.
Q3: Which statement is TRUE about gases?
- a) They have a definite shape.
- b) Their particles are fixed in place.
- c) They have high density.
- d) They fill the entire volume of a container ✅
Explanation: Gas particles move freely and occupy the full available volume.
FAQ
Q: How do you calculate gas density?
A: Using ρ = PM/RT, where P is pressure, M is molar mass, R is gas constant, and T is temperature in Kelvin.
Q: What is the difference between diffusion and effusion?
A: Diffusion is mixing via random motion; effusion is escape through a small hole without collisions.
Q: Why do lighter gases effuse faster?
A: Graham’s law: rate ∝ 1/√M, so gases with smaller molar mass effuse faster.

Pingback: Properties of Solids - CHEMASH