In organic chemistry, a reaction intermediate is a short-lived, high-energy species that is formed during the transformation of reactants into products. These intermediates are not usually isolated, but they play a crucial role in understanding reaction mechanism.
Types of Organic Reaction Intermediates
- Carbocations (Carbonium Ions)
- Carbanions
- Free Radicals
- Carbenes
- Nitrenes
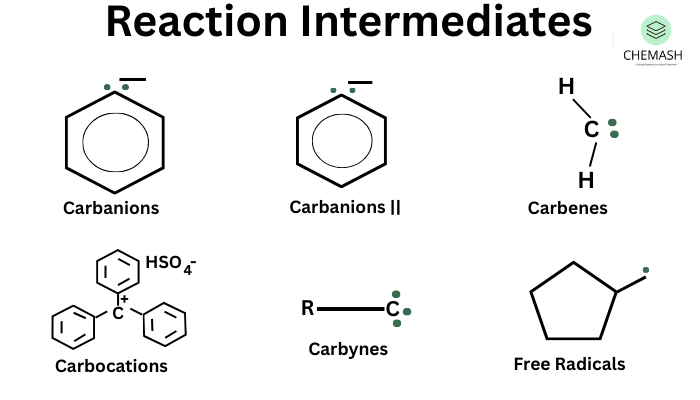
1. Carbocations (R+)
Carbocations are positively charged carbon species formed when a leaving group departs, leaving behind a carbon with only 6 electrons.
- Stability Order: 3° > 2° > 1° > methyl
- Hybridization: sp² (trigonal planar)
- Example:
CH₃–C⁺H–CH₃(secondary carbocation)
2. Carbanions (R–)
Carbanions are negatively charged carbon species with a lone pair of electrons.
- Stability Order: methyl > 1° > 2° > 3°
- Hybridization: sp³ (pyramidal)
- Example:
CH₃–
3. Free Radicals (R•)
Free radicals are species with an unpaired electron. They are neutral and highly reactive.
- Stability Order: 3° > 2° > 1° > methyl
- Hybridization: sp² or in some cases sp³
- Example:
CH₃•(methyl radical)
4. Carbenes (:CR2)
Carbenes are neutral species with two non-bonding electrons on divalent carbon atoms.
- Types: Singlet (paired) and Triplet (unpaired)
- Example: :CH₂ (methylene)
5. Nitrenes (:NR)
Nitrenes are nitrogen analogs of carbenes, formed during reactions involving azides or isocyanates.
- Structure: Neutral with a lone pair and an empty orbital.
- Example: :NH
Key Features of Intermediates
- High reactivity and short life span
- Stabilized by resonance or inductive effects
- Observed through indirect evidence (e.g. spectroscopy)
- Essential in determining reaction mechanisms
Note: The stability of intermediates influences reaction pathways and rates. For example, SN1 reactions proceed via stable carbocations.
Quiz: Reaction Intermediates
- Which intermediate has a carbon atom with a positive charge?
- What is the hybridization of a carbocation?
- Which of the following is the most stable free radical?
a) CH₃• b) CH₃CH₂• c) (CH₃)₂CH• d) (CH₃)₃C• - Which intermediate has an unpaired electron but is neutral?
- Name the nitrogen analog of a carbene.
Answers:
- Carbocation
- sp²
- d) (CH₃)₃C•
- Free radical
- Nitrene
