Resonance and Electronic Effects
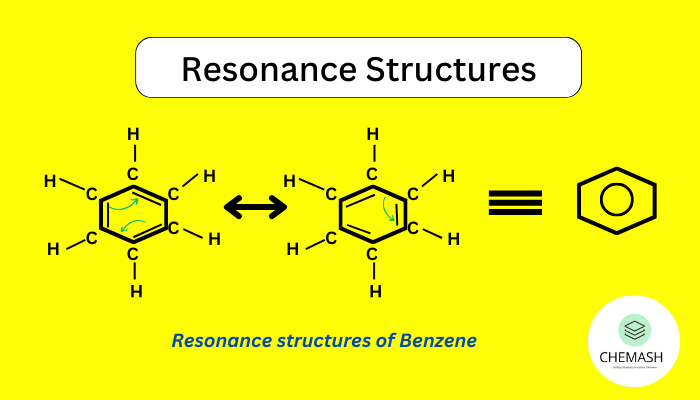
Table of Contents
What is Resonance?
Resonance is the delocalization of electrons in a molecule that cannot be explained by a single Lewis structure. Instead, resonance forms collectively represent the resonance hybrid, which is more stable than any individual form.
Key Features:
- Only π-electrons or lone pairs participate in resonance.
- The resonance hybrid is more stable than any single resonance form.
- Resonance increases stability of molecules.
Example:
In benzene (C₆H₆), resonance explains equal bond lengths:
Kekulé Structures: C₆H₆ ⇌ [Alternate double and single bonds]
Resonance hybrid: All C–C bonds are equal (between single and double).
Types of Electronic Effects
Electronic effects affect electron distribution and explain reactivity, stability, and mechanisms in organic chemistry.
1️⃣ Inductive Effect (I-Effect)
Shift of σ-electrons due to electronegativity differences.
- −I: NO₂, CN, COOH, F, Cl
- +I: Alkyl groups (–CH₃, –C₂H₅)
Example: Acidity increases with electron-withdrawing groups.
2️⃣ Mesomeric / Resonance Effect (M-Effect)
Delocalization via π-bonds or lone pairs.
- +M: –OH, –OR, –NH₂
- −M: –NO₂, –COOH, –CHO
3️⃣ Hyperconjugation
Delocalization from σ-bonds into adjacent orbitals. Known as “no bond resonance”.
Example: Stability of carbocations: 3° > 2° > 1°
4️⃣ Electromeric Effect (E-Effect)
Temporary effect in presence of reagents involving complete transfer of π-electrons.
- +E: Electrons move toward electrophile.
- −E: Electrons move away from electrophile.
Applications
- Explains electrophilic substitution reactivity.
- Predicts acid/base strength.
- Determines stability of carbocations and carbanions.
- Explains aromaticity and resonance energy.
Quiz: Resonance & Electronic Effects
1. Which compound shows resonance?
✅ Benzene
Explanation: Benzene has delocalized π-electrons.
2. Which group shows +M effect?
✅ –OH
Explanation: –OH donates electrons via resonance.
3. Carbocation stability order?
✅ 3° > 2° > 1°
Explanation: More hyperconjugation stabilizes carbocations.
4. Electromeric effect is observed:
✅ Only in presence of a reagent
5. Which stabilizes molecules by delocalizing charge?
✅ Resonance
6. –NO₂ exerts:
✅ −I and −M effect
7. Planarity of benzene is due to:
✅ Resonance and delocalization
8. Temporary effect?
✅ Electromeric effect
Fill in the Blanks
- Resonance involves delocalization of __________ electrons. (Answer: π)
- Inductive effect is due to difference in __________. (Answer: electronegativity)
- Hyperconjugation is also called __________. (Answer: no bond resonance)
- Electromeric effect occurs only in the presence of __________. (Answer: attacking reagent)
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Why is resonance important?
Resonance increases molecular stability and explains equal bond lengths in compounds like benzene.
Q2. How is inductive effect different from resonance effect?
Inductive effect involves σ-electron displacement, while resonance involves π-electrons or lone pairs.
Q3. What is the difference between +M and −M effects?
+M groups donate electrons via resonance, while −M groups withdraw them.
Q4. Which effect is temporary?
Electromeric effect, since it occurs only in the presence of a reagent.
