Standard Electrode Potential (E°)
Standard Electrode Potential (E°) measures the potential of a reversible electrode under standard conditions:
- 1 M concentration of all aqueous species
- 1 atm pressure for gases
- Temperature of 25 °C (298 K)
Definition
The Standard Electrode Potential is the potential of a half-cell measured against the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE), which has a defined potential of 0 V. It shows the tendency of a species to gain electrons (reduction) or lose electrons (oxidation) under standard conditions.
Measurement
To measure standard electrode potential, connect the half-cell of interest to the SHE and record the cell voltage. This measured value represents the electrode potential of the half-cell relative to SHE.
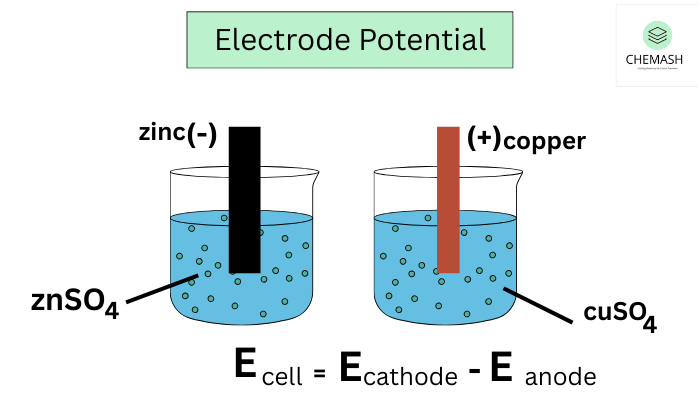
Significance of Standard Electrode Potential
- Predicts the direction of electron flow in electrochemical cells
- A positive E° means strong reduction tendency; a negative E° indicates oxidation tendency
- Helps calculate the electromotive force (EMF) of galvanic cells
- Determines the feasibility and spontaneity of redox reactions
Standard Electrode Potential Table
Scientists tabulate standard electrode potentials with respect to SHE. For example, fluorine has a very positive potential (+2.87 V), showing strong oxidizing power, while alkali metals have highly negative potentials, showing strong reducing ability.
Example
For the half-cell reaction: Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu(s), the standard electrode potential equals +0.34 V. This value shows that copper ions readily gain electrons and get reduced under standard conditions.
Quiz: Standard Electrode Potential
- What are the standard conditions for measuring standard electrode potential?
- What is the reference electrode used in measuring standard electrode potentials?
- What does a positive standard electrode potential signify?
- Why is the standard electrode potential important in electrochemistry?
- What is the standard electrode potential of the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE)?
Answers and Explanation
- 1 M concentration, 1 atm pressure, and 25 °C (298 K)
- The Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE), assigned potential 0 V
- A strong tendency of the species to undergo reduction (gain electrons)
- It predicts reaction spontaneity and helps calculate cell voltages
- By definition, 0 V
To measure E°, you pair the half-cell of interest with the SHE and record the cell voltage. That voltage becomes the standard potential of your half-cell relative to SHE (0 V reference). You can also use alternative reference electrodes (e.g. SCE, Ag/AgCl) after converting to SHE scale. (Reference Electrode — Wikipedia)
