Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics numerical problems are among the most scoring topics in Class 11 & 12 Chemistry. Moreover, almost every competitive exam such as JEE, NEET, CUET, and IIT-JAM includes direct or indirect numericals from thermodynamics. Therefore, mastering these problems significantly boosts exam performance.
This page helps students learn step-by-step numerical solving techniques using important formulas, solved examples, and exam-oriented tips.
Table of Contents
- Important Thermodynamics Formulas
- First Law of Thermodynamics Numericals
- Isothermal Process Numericals
- Adiabatic Process Numericals
- Entropy Change Numericals
- Exam-Oriented Tips
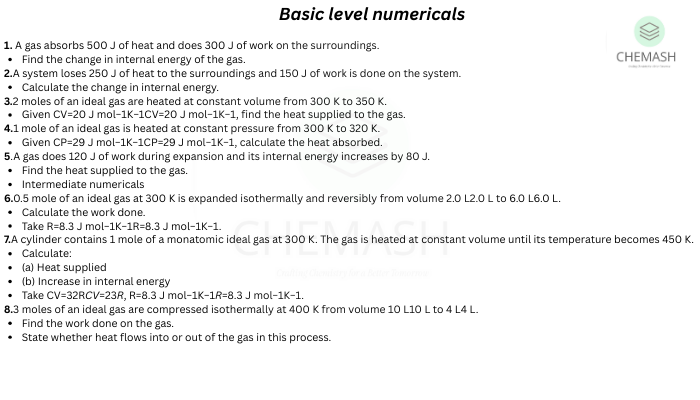

Important Thermodynamics Formulas
- First Law: ΔU = Q − W
- Isothermal Work: W = nRT ln(V2/V1)
- Adiabatic Relation: PVγ = constant
- Entropy Change: ΔS = Qrev/T
Numerical: First Law of Thermodynamics
Problem: A system absorbs 500 J of heat and does 200 J of work. Calculate the change in internal energy.
Solution:
Given: Q = +500 J, W = +200 J
Using First Law:
ΔU = Q − W = 500 − 200 = +300 J
Answer: Internal energy increases by 300 J.
Numerical: Isothermal Expansion
Problem: Calculate the work done when 1 mole of an ideal gas expands isothermally at 300 K from 10 L to 20 L.
Solution:
W = nRT ln(V2/V1)
= 1 × 8.314 × 300 × ln(2)
≈ 1728 J
Answer: Work done = 1728 J
Numerical: Adiabatic Process
Problem: In an adiabatic process, work done by the gas is 150 J. Calculate the change in internal energy.
Solution:
For adiabatic process: Q = 0
ΔU = −W = −150 J
Answer: Internal energy decreases by 150 J.
Numerical: Entropy Change
Problem: Calculate entropy change when 600 J of heat is absorbed reversibly at 300 K.
Solution:
ΔS = Q/T = 600 / 300 = 2 J K−1
Answer: Entropy change = 2 J K−1
Exam-Oriented Tips
- Always write the formula before substitution
- Follow correct sign convention carefully
- Identify the type of thermodynamic process first
- Entropy numericals are highly conceptual
