Types of Pollutants – Primary, Secondary & Classification
Pollutants are substances that contaminate the environment and harm living organisms. They can appear in air, water, or soil. Moreover, they are classified based on their nature, source, and environmental impact. Types of Pollutants
Primary Pollutants
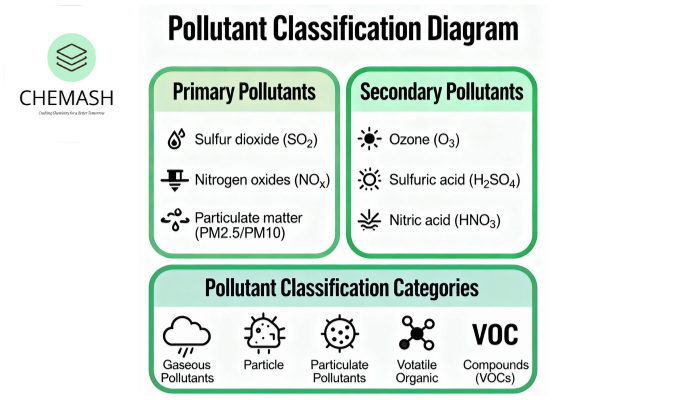
Primary pollutants originate directly from specific sources and enter the atmosphere without alteration. For example:
- Carbon monoxide (CO): Incomplete combustion of fossil fuels produces this harmful gas.
- Sulfur dioxide (SO₂): Burning coal and oil releases it, leading to respiratory problems.
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx): Vehicles and power plants emit these gases during fuel combustion.
- Particulate matter (PM): Dust, smoke, and soot contribute tiny solid or liquid particles to the air.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Solvents, paints, and industrial processes emit VOCs, which can react to form smog.
You can learn more about air pollution and its types on Britannica.
Secondary Pollutants
In contrast, secondary pollutants form when primary pollutants react with natural atmospheric components. Consequently, they appear as a result of chemical reactions in sunlight or moisture:
- Ozone (O₃): Sunlight triggers a reaction between nitrogen oxides and VOCs, forming ozone in the lower atmosphere.
- Smog: When smoke and fog combine, they create smog, which reduces visibility and harms health.
- Acid rain: Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides react with water vapor, producing acidic rainfall that damages ecosystems.
Biodegradable and Non-Biodegradable Pollutants
Pollutants are also classified based on how easily nature can break them down. For instance:
- Biodegradable Pollutants: Natural processes, such as bacterial decomposition, can break them down easily (e.g., food waste, sewage).
- Non-Biodegradable Pollutants: These substances persist for decades and accumulate in the environment (e.g., plastics, heavy metals).
Other Classifications
Furthermore, pollutants can be grouped according to their physical or chemical state:
- Gaseous Pollutants: Include CO, SO₂, NOx, and methane (CH₄).
- Particulate Pollutants: Dust, smoke, and aerosols fall under this type.
- Heavy Metal Pollutants: Lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), and cadmium (Cd) pose serious health hazards.
Quiz – Types of Pollutants
- Which pollutant is a primary pollutant?
a) Ozone
b) Sulfur dioxide
c) Acid rain
d) Smog
Answer: b)
Explanation: Sulfur dioxide directly enters the air when coal or oil burns. - Ozone in the lower atmosphere is classified as:
a) Primary pollutant
b) Secondary pollutant
c) Biodegradable pollutant
d) Heavy metal pollutant
Answer: b)
Explanation: It forms due to reactions between primary pollutants and sunlight. - Which pollutant is non-biodegradable?
a) Food waste
b) Sewage
c) Lead
d) Paper waste
Answer: c)
Explanation: Lead remains in the environment for years and does not decompose naturally. - Particulate matter mainly consists of:
a) Gaseous substances
b) Tiny solid and liquid particles
c) Organic gases
d) Water vapor
Answer: b)
Explanation: Particulate matter includes microscopic dust, smoke, and aerosols.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are pollutants?
Pollutants are harmful substances that enter air, water, or soil. They disrupt natural systems and damage living organisms.
Q2. What is the difference between primary and secondary pollutants?
Primary pollutants are released directly into the air, whereas secondary pollutants result from chemical reactions among primary ones.
Q3. What are examples of non-biodegradable pollutants?
Common examples include plastics, lead, and mercury. These substances persist for a long time and accumulate in ecosystems.
Q4. How can pollution be reduced?
To reduce pollution, use renewable energy, recycle waste, enforce emission controls, and plant more trees. As a result, air and water quality improve significantly.
Related reading: Effects of Air Pollution |
