Types of Systems in Thermodynamics (Open, Closed & Isolated)
Thermodynamics a system refers to the specific part of the universe chosen for detailed study, while everything outside it is called the surroundings. Understanding different types of thermodynamic systems is essential for Class 11 Chemistry, NEET, JEE Main & Advanced, and competitive exams.Types of Systems in Thermodynamics
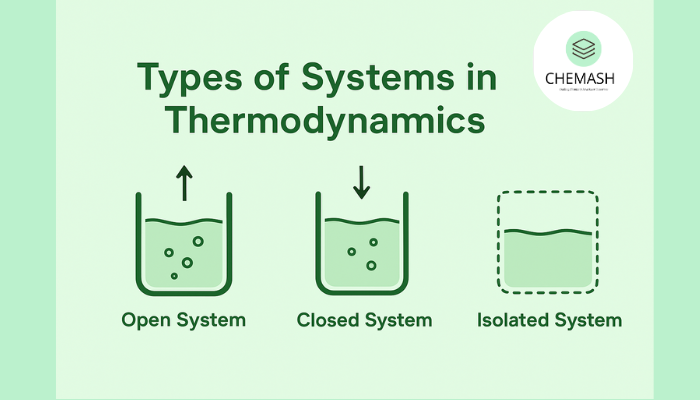
Systems are classified based on whether they allow matter exchange and energy exchange (heat or work) with their surroundings.
Table of Contents
- What is a Thermodynamic System?
- Open System
- Closed System
- Isolated System
- Comparison Table
- NEET & JEE Exam Tricks
- Problem-Solving Examples
- MCQ Quiz (Exam Ready)
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Thermodynamic System?
A thermodynamic system is a well-defined region of space or quantity of matter chosen for analysis. The boundary of the system may be real or imaginary, fixed or movable.
Depending on interaction with surroundings, systems are classified into: Open system, Closed system, and Isolated system.
Open System
An open system can exchange both matter and energy with its surroundings. Mass transfer and heat/work transfer occur simultaneously.
Key Characteristics
- ✔ Matter exchange allowed
- ✔ Energy exchange allowed
- ✔ Mass of system changes
Examples
- Boiling water in an open pot
- Human body
- Car engine
- Open chemical reactor
In NEET and JEE exams, living organisms are always treated as open systems.
Closed System
A closed system allows energy exchange (heat or work) but does not allow matter exchange. The mass of the system remains constant.
Key Characteristics
- ❌ No matter exchange
- ✔ Energy exchange allowed
- ✔ Mass remains constant
Examples
- Gas in a sealed piston
- Water in a closed container being heated
- Refrigerator (approximation)
Important Exam Point: A refrigerator is treated as a closed system in thermodynamics.
Isolated System
An isolated system cannot exchange either matter or energy with its surroundings. It is completely cut off from the environment.
Key Characteristics
- No matter exchange
- No energy exchange
- Total energy remains constant
Examples
- Perfectly insulated thermos flask
- Universe (ultimate isolated system)
Exam Trick: If a question mentions perfect insulation → it is an isolated system.
Summary Comparison Table
| System Type | Matter Exchange | Energy Exchange | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open System | Yes | Yes | Boiling water without lid |
| Closed System | No | Yes | Sealed heated container |
| Isolated System | No | No | Thermos flask |
NEET & JEE Exam Tricks
- Living organisms → Open system
- Gas in piston → Closed system
- Thermos / Universe → Isolated system
- If mass changes → Open system
- If insulation mentioned → Isolated system
Concept-Based Problem Example
Question: A gas is heated in a sealed container. Identify the system.
Answer: Matter cannot escape, but heat is supplied → Closed system.
MCQ Quiz – Types of Systems
Q1. Which system exchanges both matter and energy?
a) Closed b) Isolated c) Open d) None
Answer: c) Open system
Q2. A thermos flask is an example of:
a) Open b) Closed c) Isolated d) None
Answer: c) Isolated system
Q3. Refrigerator is treated as:
a) Open b) Closed c) Isolated
Answer: b) Closed system
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the three types of systems in thermodynamics?
Open, Closed, and Isolated systems.
Is the universe an isolated system?
Yes, the universe is considered a perfectly isolated system.
Is human body an open system?
Yes, because it exchanges both matter and energy.
Related Thermodynamics Topics
Wikipedia – Thermodynamic System
